Nerve pain, also known as neuropathic pain, is a type of chronic pain that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and injury to the nerves. While there are several medications available to manage nerve pain, many people are turning to alternative treatments, such as cannabis, to alleviate their symptoms. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is a compound found in the cannabis plant that has been shown to have pain-relieving properties. In this article, we will explore the use of THC for nerve pain and the research that supports its effectiveness as a treatment option. We will also examine the potential risks and side effects of using THC for pain management.
Nerve pain symptoms
Nerve pain, also known as neuropathic pain, is a type of chronic pain that occurs due to damage or dysfunction in the nervous system. The symptoms of nerve pain can vary depending on the underlying cause and location of the affected nerves. Here are some common symptoms of nerve pain:
- Shooting or stabbing pain: Nerve pain is often described as a sharp, shooting, or stabbing pain that may come and go or be constant.
- Burning sensation: Nerve pain can also cause a burning sensation, which may feel like a hot or cold sensation on the skin. This symptom can be persistent or intermittent and may worsen at night.
- Tingling or numbness: People with nerve pain may also experience a tingling or numbness sensation, which can be described as a “pins and needles” feeling.
- Sensitivity to touch: Nerve pain can make the affected area more sensitive to touch or pressure, making it difficult to wear certain clothing or even engage in daily activities.
- Muscle weakness: Nerve damage can also cause muscle weakness and difficulty with fine motor skills, such as buttoning a shirt or holding a pen.
- Changes in coordination or balance: In some cases, nerve pain can lead to changes in coordination and balance, which can make it difficult to walk or perform other physical activities.
Causes and treatment of nerve pain
Nerve pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury or damage to the nerves, infections, autoimmune disorders, and certain medications. Some common causes of nerve pain include:
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves over time, leading to nerve pain.
- Trauma or injury: Physical injuries or trauma, such as car accidents, falls, or sports injuries, can damage nerves and lead to nerve pain.
- Infections: Certain infections, such as shingles, HIV/AIDS, and Lyme disease, can damage nerves and cause pain.
- Autoimmune disorders: Conditions such as multiple sclerosis and lupus can cause the immune system to attack and damage nerves, leading to nerve pain.
- Medications: Some medications, including chemotherapy drugs and certain antibiotics, can cause nerve damage and lead to nerve pain.
The treatment of nerve pain depends on the underlying cause and severity of the symptoms. Some common treatment options include:
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and opioids to manage nerve pain.
- Therapy: Physical therapy or occupational therapy can help improve muscle strength, coordination, and range of motion, which can reduce nerve pain.
- Lifestyle changes: Making changes such as quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and exercising regularly can help manage nerve pain.
- Alternative therapies: Some people find relief from nerve pain through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage therapy, or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS).
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair damaged nerves or remove tumors that are causing nerve pain.
Cannabis and its cannabinoids
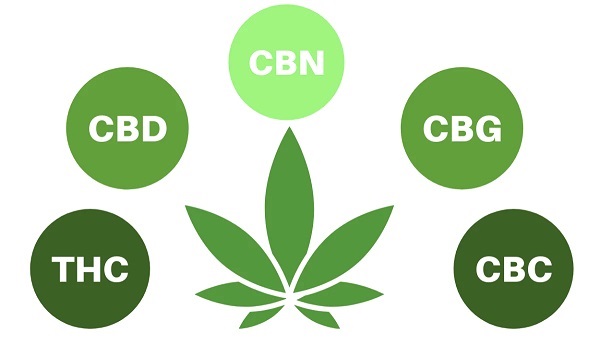
Cannabis is a plant that contains over 100 chemical compounds known as cannabinoids. The two most well-known cannabinoids are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). THC is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, responsible for the “high” associated with marijuana use, while CBD does not have psychoactive effects.
In addition to THC and CBD, there are other cannabinoids found in cannabis, including cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), and cannabichromene (CBC), among others. Each of these compounds has unique properties and potential therapeutic benefits.
Cannabis and its cannabinoids have been used for medicinal purposes for thousands of years. They have been used to treat pain, nausea, inflammation, and a variety of other conditions. In recent years, there has been growing interest in the potential therapeutic benefits of cannabis and its cannabinoids, particularly for conditions such as epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, and chronic pain.
However, the use of cannabis and its cannabinoids for medicinal purposes remains controversial due to the potential risks and side effects associated with their use, as well as legal considerations.
How do cannabinoids affect the perception of pain?
Cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD, have been shown to have an impact on the perception of pain by interacting with the body’s endocannabinoid system. The endocannabinoid system is a complex network of receptors, enzymes, and molecules that help regulate a variety of physiological processes, including pain perception.
Cannabinoids work by binding to and activating cannabinoid receptors, which are primarily located in the brain and nervous system. The two primary types of cannabinoid receptors are CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors are found primarily in the central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are found primarily in the peripheral nervous system, immune cells, and other tissues.
THC is a partial agonist of CB1 receptors and can activate them to produce a variety of effects, including the modulation of pain signaling. Studies have shown that THC can reduce pain associated with conditions such as neuropathic pain, cancer-related pain, and inflammatory pain.
CBD, on the other hand, does not directly activate CB1 or CB2 receptors but can still modulate pain signaling through a variety of other mechanisms. CBD has been shown to reduce inflammation, which can contribute to pain, and can also enhance the effects of endocannabinoids, which are natural cannabinoids produced by the body.
In addition to these direct effects on pain signaling, cannabinoids have also been shown to have neuroprotective properties that can help reduce pain and protect against nerve damage. For example, studies have suggested that CBD may be effective in reducing neuropathic pain associated with conditions such as multiple sclerosis and neuropathy.
Overall, the mechanisms by which cannabinoids modulate pain perception are complex and multifaceted, and more research is needed to fully understand their effects on pain. However, studies have suggested that cannabinoids may be effective in reducing pain associated with a variety of conditions and may offer a promising avenue for the treatment of chronic pain. It is important to note that the use of cannabinoids for pain management should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as they can interact with other medications and may not be appropriate for everyone.
Neuropathic pain reduction

One of the primary ways that cannabinoids reduce neuropathic pain is through their effects on the endocannabinoid system. The endocannabinoid system plays a crucial role in regulating pain perception, and cannabinoid receptors are found throughout the nervous system. By binding to these receptors, cannabinoids can help modulate pain signaling and reduce the perception of pain.
THC, in particular, has been shown to be effective in reducing neuropathic pain in a number of studies. A 2018 review of randomized controlled trials found that THC was associated with a statistically significant reduction in neuropathic pain compared to placebo.
CBD has also been shown to be effective in reducing neuropathic pain, although the mechanisms by which it does so are not yet fully understood. Some research suggests that CBD may reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which can contribute to neuropathic pain. CBD may also modulate the activity of other neurotransmitter systems involved in pain signaling, such as the serotonin and opioid systems.
In addition to THC and CBD, other cannabinoids such as cannabichromene (CBC) and cannabigerol (CBG) have also shown promise in reducing neuropathic pain. CBC has been shown to have potent analgesic effects in animal models of neuropathic pain, while CBG has been shown to reduce inflammation and pain in models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain.
Overall, while more research is needed to fully understand the effects of cannabinoids on neuropathic pain.
HIV neuropathy
HIV neuropathy is a type of neuropathic pain that occurs as a complication of HIV infection. It is estimated that up to 30% of people with HIV experience neuropathic pain at some point during the course of their disease.
HIV neuropathy can manifest in a variety of ways, including numbness, tingling, and burning sensations in the hands and feet, as well as weakness and pain in the muscles. It is thought to be caused by a combination of factors, including direct damage to nerves by the virus, inflammation, and toxic effects of certain antiretroviral medications.
While traditional pain medications may be effective in some cases, they can also have significant side effects and may not be well-tolerated by some patients. As a result, there has been increasing interest in the potential use of cannabinoids such as THC and CBD for the treatment of HIV neuropathy.
Studies have suggested that cannabinoids may be effective in reducing neuropathic pain associated with HIV infection. For example, a 2007 study published in the journal Neurology found that smoked cannabis was associated with a significant reduction in pain intensity and improved sleep quality in patients with HIV-related neuropathy. Another study published in the Journal of Pain in 2013 found that a combination of THC and CBD was more effective than placebo in reducing pain intensity and improving sleep quality in patients with HIV-associated neuropathy.
The mechanisms by which cannabinoids reduce neuropathic pain in the context of HIV infection are not yet fully understood, but they are thought to involve a combination of effects on pain signaling, inflammation, and neuroprotection. For example, cannabinoids have been shown to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which can contribute to nerve damage and pain.
Overall, while more research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits and risks of using cannabinoids for HIV neuropathy, current evidence suggests that they may be a promising option for the management of this challenging condition.
Nerve pain in the legs
Nerve pain in the legs is a common condition that can be caused by a variety of factors, including nerve damage or compression, inflammation, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes or multiple sclerosis.
Symptoms of nerve pain in the legs can vary depending on the underlying cause, but often include tingling, burning, or shooting pain that may be accompanied by weakness, numbness, or difficulty walking. The pain may be constant or intermittent, and may worsen at night or with movement.
Treatment for nerve pain in the legs typically involves addressing the underlying cause, as well as managing the symptoms of pain. In some cases, pain medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or opioids may be prescribed to help manage pain. However, these medications can have significant side effects and may not be well-tolerated by all patients.
As a result, there has been increasing interest in the potential use of alternative therapies such as cannabinoids for the treatment of nerve pain in the legs. Studies have suggested that cannabinoids such as THC and CBD may be effective in reducing neuropathic pain associated with nerve damage.
For example, a 2017 study published in the European Journal of Pain found that a combination of THC and CBD was more effective than placebo in reducing pain intensity and improving sleep in patients with peripheral neuropathy, a condition that can cause nerve pain in the legs. Another study published in the Journal of Pain in 2015 found that THC alone was associated with a significant reduction in pain intensity and improved sleep quality in patients with neuropathic pain.
Post-traumatic or post-surgical nerve pain
Post-traumatic or post-surgical nerve pain is a type of neuropathic pain that occurs as a result of physical injury or surgery. It can manifest in a variety of ways, including tingling, burning, or shooting pain, as well as hypersensitivity to touch or temperature changes.
Post-traumatic or post-surgical nerve pain can be caused by a number of factors, including direct damage to nerves during the traumatic event or surgery, inflammation, and scarring. It can also be exacerbated by factors such as stress and anxiety.
Treatment for post-traumatic or post-surgical nerve pain typically involves a combination of approaches aimed at addressing the underlying cause of the pain, as well as managing the symptoms. This may include medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or opioids to help manage pain, as well as physical therapy or other forms of rehabilitative therapy to help improve mobility and function.
In some cases, cannabinoids such as THC and CBD may be used as an alternative or complementary therapy for post-traumatic or post-surgical nerve pain. Studies have suggested that cannabinoids may be effective in reducing neuropathic pain associated with nerve damage.
Treatment-resistant neuropathy
Treatment-resistant neuropathy is a condition where the patient does not respond well to standard treatments for neuropathic pain. It can be a challenging condition to manage, as traditional pain medications such as opioids may not be effective or may have significant side effects.
In cases of treatment-resistant neuropathy, alternative therapies may be considered. One potential alternative therapy is the use of cannabinoids such as THC and CBD. Studies have suggested that cannabinoids may be effective in reducing neuropathic pain associated with nerve damage, and may be a promising option for the management of treatment-resistant neuropathy.
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is a type of nerve damage that can occur in people with diabetes. It affects the nerves that control sensation, movement, and organ function, and can cause symptoms such as pain, tingling, numbness, and weakness in the hands and feet.
The underlying mechanisms that cause DPN are not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of factors including high blood sugar levels, inflammation, and oxidative stress. Over time, these factors can damage the nerves, leading to the symptoms of DPN.
Treatment for DPN typically involves a combination of approaches aimed at controlling blood sugar levels, managing pain, and addressing other symptoms. This may include medications such as anticonvulsants, antidepressants, and opioids to help manage pain, as well as physical therapy or other forms of rehabilitative therapy to help improve mobility and function.
Cannabinoids such as THC and CBD may also be used as an alternative or complementary therapy for DPN. Studies have suggested that cannabinoids may be effective in reducing neuropathic pain associated with nerve damage.
The mechanisms by which cannabinoids reduce nerve pain in the context of DPN are not fully understood, but they are thought to involve modulation of pain signaling, inflammation, and neuroprotection. For example, cannabinoids have been shown to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which can contribute to nerve damage and pain.
What type of medical marijuana is used for nerve pain?

The type of medical marijuana used for nerve pain may vary depending on the individual and the specific symptoms they are experiencing. However, research suggests that medical marijuana strains with high levels of THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and/or CBD (cannabidiol) may be effective in reducing neuropathic pain.
Some medical marijuana strains that have been shown to be effective in reducing nerve pain include:
- Harlequin: a strain that has a balanced THC-to-CBD ratio, making it a good option for those who want to avoid the psychoactive effects of THC.
- ACDC: a high-CBD strain that has minimal psychoactive effects and is often used for pain relief.
- Sour Diesel: a strain with a high THC content that has been shown to be effective in reducing neuropathic pain.
It is important to note that the use of medical marijuana for nerve pain should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as it may interact with other medications and may not be appropriate for everyone. Additionally, the specific strain and dosing may need to be adjusted based on the individual’s response and tolerance.
Summary
Medical marijuana, specifically strains high in THC and/or CBD, has been shown to be effective in reducing neuropathic pain. The specific strain and dosing may vary depending on the individual and their symptoms. It is important to use medical marijuana under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as it can interact with other medications and may not be appropriate for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the best strains for nerve pain?
The best strains for nerve pain may vary depending on the individual and their specific symptoms. However, some medical marijuana strains have been shown to be effective in reducing neuropathic pain.
- Harlequin: A strain that has a balanced THC-to-CBD ratio, making it a good option for those who want to avoid the psychoactive effects of THC.
- ACDC: A high-CBD strain that has minimal psychoactive effects and is often used for pain relief.
- Sour Diesel: A strain with a high THC content that has been shown to be effective in reducing neuropathic pain.
- Blue Dream: A strain with a balanced THC-to-CBD ratio that can provide pain relief and a mild euphoric effect.
- Girl Scout Cookies: A high-THC strain that has been reported to have strong pain-relieving effects.
Should I use sativa or indica for nerve pain?
The choice between sativa or indica strains for nerve pain may depend on the individual’s preference and the specific symptoms they are experiencing. Sativa strains tend to have higher levels of THC and can provide more of a cerebral, uplifting effect. Indica strains, on the other hand, tend to have higher levels of CBD and can provide more of a relaxing, sedative effect.
Some people may find that sativa strains are more effective in reducing their nerve pain because of the pain-relieving and mood-elevating properties of THC. Others may prefer indica strains for their ability to induce relaxation and relieve anxiety, which can also help to alleviate nerve pain.
It’s important to note that the effects of sativa and indica strains can vary depending on the specific strain, dose, and individual response.
Can edibles help with nerve pain?
Edibles can potentially help with nerve pain, as they provide a longer-lasting and more intense effect than other methods of consuming medical marijuana. When ingested, the cannabinoids in edibles are metabolized in the liver and converted into a more potent form that can provide longer-lasting pain relief.
However, it’s important to be cautious when using edibles for nerve pain. The effects of edibles can take longer to onset and may vary depending on the individual’s metabolism and the potency of the edible. It can be easy to accidentally consume too much, which can lead to unwanted side effects such as anxiety, paranoia, or drowsiness.
Which is better: CBD oil vs gabapentin for nerve pain?
CBD oil and gabapentin are two different options for treating nerve pain, and the choice between them may depend on the individual’s specific symptoms and personal preferences.
CBD oil is a natural product derived from the hemp plant and contains cannabinoids such as CBD, which has been shown to have pain-relieving properties. CBD oil is generally considered safe and has fewer side effects compared to prescription medications such as gabapentin. Additionally, CBD oil does not have the potential for abuse or dependence that prescription medications do.
Gabapentin is a prescription medication that is commonly used to treat nerve pain. It works by reducing the activity of nerves that are responsible for transmitting pain signals to the brain. While it can be effective in reducing nerve pain, it may cause side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and fatigue. Additionally, gabapentin can be habit-forming and may have interactions with other medications.
Ultimately, the choice between CBD oil and gabapentin for nerve pain may require a consultation with a healthcare professional to determine what treatment option may be best for the individual. In some cases, a combination of both CBD oil and gabapentin may be appropriate.
Does CBD oil help with pinched nerve pain?
CBD oil may help with pinched nerve pain, as it has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties that can help to reduce pain and inflammation. Pinched nerves occur when excessive pressure is placed on a nerve, causing pain, numbness, and tingling sensations in the affected area. CBD oil can potentially help to alleviate these symptoms by reducing inflammation and pain in the affected area.