The legalization and increasing acceptance of cannabis for medicinal and recreational use have sparked a wave of innovation in the cannabis industry. One notable development is the emergence of liquid THC, a potent and versatile form of cannabis extract that offers a range of unique benefits and consumption methods. Liquid THC, also known as cannabis tincture has gained popularity among users seeking a discreet, convenient, and customizable cannabis experience.
Traditionally, cannabis consumption involved smoking or vaporizing the plant’s flowers, but liquid THC presents an alternative option for those who prefer not to inhale smoke or vapor. This concentrated form of cannabis offers a potent dose of Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, providing users with a controlled and consistent experience.
In this article, we delve into the world of liquid THC, exploring its production methods, applications, and effects. We will also address concerns and precautions associated with its use, shedding light on the responsible and informed consumption of this powerful cannabis extract.
What is liquid THC?
When it comes to the technical aspects, liquid THC can be specifically classified as a tincture. A tincture is essentially a liquid extract that is created by immersing a substance in alcohol to extract its active ingredient. In the case of liquid THC tinctures, the active ingredient being extracted is THC, which is obtained from potent cannabis strains like Bruce Banner or Death Star. These strains are known for their high THC content.
On the other hand, if one intends to create a CBD tincture, they would use a high-CBD/low-THC strain such as Charlotte’s Web or Sour Tsunami. These strains are specifically bred to contain a significant amount of CBD while minimizing the THC content. By using these strains, it is possible to create a tincture that primarily contains CBD as its active ingredient.
It is important to note that the range of tinctures is not limited to cannabis-based options. In fact, virtually any plant, combination of plants, or even animal material can be used to create a tincture. Commonly used medicinal tinctures include those derived from garlic, hyssop, and sage, each offering their own unique properties and benefits.
Although alcohol is the most commonly used solvent for making tinctures, other liquids such as oils, vinegars, and glycerins can also be employed. This allows for a diverse range of tincture preparations catering to different preferences and requirements. Additionally, various types of alcohol can be utilized in the creation of tinctures, including but not limited to vodka, brandy, and ethanol. The choice of alcohol can depend on factors such as desired potency, flavor, and intended use of the tincture.
How is liquid THC made?

There are several methods available for creating tinctures, including liquid THC tinctures. Let’s explore three popular techniques: the traditional room-temperature method, the cold-brew method, and the accelerated hot method. Here, I’ll provide a description and recipe for each.
The Room-Temperature Method
If you prefer a more traditional approach to creating liquid THC tinctures, the room-temperature method offers simplicity and effectiveness. This method doesn’t require any advanced technology and can be likened to brewing tea. It ensures that every last molecule of THC is extracted from the plant. However, it does take significantly longer to produce the final product compared to other methods. If time is of the essence, the cold or hot method may be more suitable. Here’s a step-by-step guide on making liquid THC using the room-temperature method:
- Start by chopping your cannabis plant matter into small pieces and decarboxylate it in a preheated oven at 230℉ (110℃) for about 35 minutes. Decarboxylation activates the THC and enhances its potency.
- Place the decarboxylated cannabis into a quart-sized (32 ounce) mason jar.
- Pour in 32 ounces of the highest-proof alcohol you can obtain. It is recommended to use high-proof options like Everclear, while avoiding Isopropyl alcohol, which is toxic.
- Securely cover the jar, preferably with a screw-on lid, to prevent any leaks or spills.
- Shake the jar vigorously to ensure thorough mixing of the cannabis and alcohol.
- Place the mason jar inside a brown paper bag and store it in a dark cabinet or closet. This step is crucial to protect the tincture from sunlight, which could degrade its potency.
- Monitor the storage location to ensure it remains at room temperature, not excessively hot.
- Allow the mason jar to sit undisturbed for a period of 30 to 60 days, or even longer if possible. The longer the steeping period, the stronger and more potent the resulting tincture will be.
- Once the steeping period is complete, strain the liquid by pouring it through a cheesecloth to separate the plant matter from the remaining tincture.
- Store the resulting liquid in an opaque bottle, away from direct sunlight, to preserve its potency and quality.
The Cold Method
If you prefer a cold method for creating liquid THC tinctures, this technique involves freezing the cannabis plant material to preserve the cannabinoids’ integrity. Here’s a step-by-step procedure to follow:
- Begin by drying and decarboxylating your plant matter. This process ensures that the cannabinoids are activated and ready for extraction.
- Grind the dried plant matter and place it in a zip-top plastic bag. Store the bag in the freezer for a few hours until the plant matter is frozen stiff.
- Similarly, place your chosen bottle of alcohol in the freezer. It won’t freeze solid due to its lower freezing point.
- Once the plant matter is frozen, take a quart-sized (32 ounces) mason jar and mix 1 ounce of the frozen cannabis with the quart of alcohol.
- Seal the mason jar tightly with a lid and shake it vigorously for approximately 5 minutes. This ensures proper mixing of the cannabis and alcohol.
- Return the sealed jar to the freezer.
- Every 2 to 3 hours, remove the jar from the freezer and give it a good shake. This intermittent shaking helps with the extraction process.
- Repeat the cycle of shaking and storing in the freezer for the next two days, amounting to a total steeping period of 48 hours.
- After 48 hours, separate the solid plant material from the liquid by pouring the contents of the jar through a cheesecloth. Discard the strained plant matter.
- For further filtration, pour the liquid through a coffee filter to remove any remaining small plant particles.
- Finally, store the resulting tincture in an opaque bottle to protect it from light exposure. Prolonged exposure to light can degrade the tincture’s potency and quality.
The Hot Method
The hot method, also known as “green dragon,” offers a quicker alternative to the traditional tincture-making process. Instead of waiting weeks for the mixture to steep, heat is applied to expedite the extraction. However, it is important to note that the hot method comes with certain risks, including the potential for alcohol catching fire during the heating process and the increased likelihood of diminishing the medicinal benefits of the tincture through cooking.
Despite these risks, the hot method is relatively simple and can produce a cannabis tincture in just 30 to 60 minutes, significantly reducing the waiting time compared to other methods. If you prefer a faster process and are willing to manage the associated risks, this method might be suitable for you.
It is advisable to start with small quantities and gain some experience before scaling up the recipe. For this demonstration, we will use ⅛ ounce of cannabis and 2 ounces of high-proof alcohol. Once you are familiar with the process, you can increase the amounts accordingly. Ensure you have proper ventilation during the procedure.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating a cannabis tincture using the hot method:
- Begin by drying and decarboxylating ⅛ ounce of cannabis to activate the cannabinoids.
- Chop the dried plant matter using a coffee grinder or marijuana grinder to achieve a finer consistency.
- In a 1-pint mason jar, combine the chopped cannabis with 2 ounces of the highest-proof alcohol available.
- Prepare a water bath by filling a medium-sized saucepan with about 1 inch of water and bringing it to a low simmer.
- Ensure the oven fan is set to high for proper ventilation.
- Insert a quick-read or candy thermometer into the mason jar and carefully place the jar into the simmering water, creating a water bath.
- Monitor the liquid temperature inside the mason jar and raise it to 170℉. Pure ethanol boils at 173℉, so it’s essential to keep the temperature just below the boiling point.
- Maintain the simmering water bath and the alcohol temperature around 170℉ for 20 minutes, ensuring consistent heat.
- After 20 minutes, separate the plant matter from the liquid THC by using a mesh strainer or cheesecloth to strain the contents of the mason jar.
- Transfer the resulting tincture into an opaque dropper bottle to protect it from light.
The basic production principles
Irrespective of the method you choose, the fundamental principles of tincture production remain consistent. During the steeping or cooking process, the cannabinoids present in the cannabis plant are released. These released cannabinoids are then absorbed by the alcohol, effectively extracting their potent properties. Subsequently, the plant matter is separated and discarded, leaving behind a concentrated and powerful liquid known as a tincture. The tincture is significantly more potent than its individual components, representing a concentrated form of cannabis extract.
Liquid THC tinctures have been tested and found to contain high levels of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), often reaching up to 90% THC content. In comparison, oils, waxes, and shatters typically contain around 50% THC, while the THC content of smoked cannabis buds ranges from 12% to 25%. This demonstrates the potency and concentration achieved through the tincture-making process.
Storing liquid THC

To ensure ease of access and precise dosage, tinctures are commonly stored in dropper bottles. This practical packaging facilitates consumption and allows for accurate measurement. A standard eyedropper typically holds approximately 1 milliliter (or 1 gram) of liquid, providing a convenient dosage amount for tinctures.
Alternatively, you have the option of storing your tincture in a small spray bottle, enabling you to administer the liquid THC by squirting it into your mouth, similar to using breath spray. However, regardless of the chosen storage method, it is crucial to never drip the tincture into your eyes. The recommended method of consumption is to take the tincture sublingually, placing it under the tongue for absorption.
When stored in an opaque bottle and kept away from direct sunlight, your tincture should maintain its potency for an extended period. In fact, it is likely that you will use up the tincture before it reaches its expiration date, unless you consume it sparingly (such as taking only one dropper-full per year).
By following these storage practices, you can ensure the longevity and effectiveness of your tincture, allowing for convenient access and proper dosage whenever needed.
What does liquid THC look like?
Liquid THC typically exhibits various shades of green, reflecting the characteristics of the plant matter used in its production. The color can range from light to dark green, and in some cases, it may even have a greenish-brown hue. A well-made liquid THC tincture should possess the distinct aroma of cannabis, emitting a somewhat floral scent.
However, it is important to exercise caution when purchasing liquid THC, as there have been instances where unscrupulous sellers have misrepresented their products. Some unsuspecting cannabis consumers have unknowingly purchased “liquid THC” from unreliable sources, only to discover that what they acquired was nothing more than water or some other liquid lacking the desired properties. To avoid falling victim to such situations, it is essential to ensure that the liquid you purchase exhibits at least a green color, which indicates the presence of cannabis extract. Whenever possible, it is advisable to purchase liquid THC from reputable and trustworthy sources to guarantee authenticity and quality.
How to use?
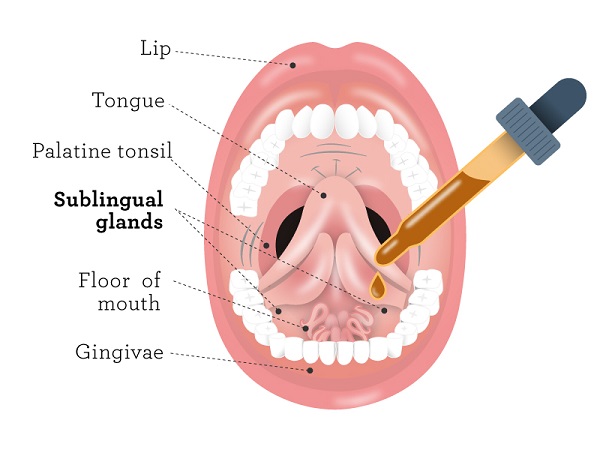
Liquid THC offers versatile consumption methods, with oral ingestion and vaporization being the most common approaches.
Oral consumption is the traditional and widely practiced method for experiencing the effects of liquid THC. It involves placing 2-3 drops of the tincture under the tongue, allowing for rapid absorption due to the abundant blood supply in the soft tissues in that area. It’s important to note that despite the fast absorption, the onset of psychoactive effects may take some time. It is crucial to avoid the temptation of taking more in an attempt to hasten the process, as it can lead to an unpleasant experience. Additionally, liquid THC can be sprayed onto food to create a cannabis-infused meal. When using this method, start with 1-2 sprays on your favorite dish. It’s worth mentioning that ingesting liquid THC in this manner is more akin to traditional edibles, resulting in a potentially slower onset of psychoactive effects that may last longer.
Vaporization using electronic vape pens is a relatively recent method of consuming liquid THC. In this process, the liquid THC is vaporized within the pen and then smoked, similar to regular e-liquids.
Both oral consumption and vaporization provide distinct experiences when consuming liquid THC, offering users the flexibility to choose the method that best suits their preferences and desired effects.
What are the effects of liquid THC?
When you consume liquid THC, the effects will be similar to those experienced when smoking a high-THC strain. THC, being the primary component in liquid THC, can cause effects such as time distortion, heightened sensitivity to stimuli, drowsiness, and euphoria.
It’s important to note that liquid THC lacks the other active ingredients found in marijuana, such as CBD, cannabinol, cannabiverin, and cannabigerol, among others. These additional compounds in marijuana have their own unique physiological and psychological effects, which cannot be experienced with liquid THC alone.
For instance, CBD has various potential benefits, including reducing nausea and vomiting, suppressing seizures, managing psychosis disorders, and combating inflammation, among other effects. However, liquid THC does not provide these additional benefits.
The onset of effects with liquid THC depends on the method of consumption. When taken sublingually (under the tongue), effects can be felt within 15-45 minutes and reach their peak at approximately 90 minutes. If consumed with food, the effects take longer to manifest but can last for 2-4 hours.
However, exercise caution to avoid consuming too much and potentially having a negative experience. The intensity of the highs produced by liquid THC, whether through tinctures or edibles, can vary based on factors like metabolism, body composition, and individual differences. What works for one person may not work as well for you, so it’s important to start with a small dose and gradually increase if needed.
What are the dangers of liquid THC?
It’s essential to approach the use of liquid THC with caution due to its highly-concentrated nature.
At its most extreme, there is the potential for a “bad trip” when using liquid THC. Since liquid THC lacks the balancing effects of CBD and other compounds found in marijuana, it can lead to intense anxiety or paranoia. The high concentration of THC in the liquid can also induce vomiting and, in severe cases, even cause unconsciousness. It’s important to note that this unconsciousness is different from regular sleep and can be a cause for concern.
Regardless of your experience level with liquid THC or the method of consumption you choose, it is strongly recommended to exercise caution and approach it with respect. Even experienced users can have negative experiences, so it’s crucial to start with a low dose and gradually increase if needed. Taking it slow allows you to gauge your tolerance and understand how the substance affects you personally.
Remember to prioritize your safety and well-being when using liquid THC. If you have any concerns or are unsure about its effects, it’s advisable to seek guidance from a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
Liquid THC provides a concentrated form of THC without the presence of other active ingredients found in marijuana, such as CBD and various cannabinoids. While liquid THC can produce similar effects to smoking high-THC strains, it’s important to note that the absence of additional compounds limits its potential therapeutic benefits.
While liquid THC offers potent THC effects, it’s vital to be mindful of its limitations and potential risks. Responsible use, careful dosage management, and awareness of personal tolerance are crucial for a safe and enjoyable experience with this powerful liquid. Consulting with healthcare professionals or seeking guidance from reputable sources is always recommended to ensure informed and responsible consumption.