Cannabis has been used for recreational and medicinal purposes for thousands of years, and its popularity has only continued to grow in recent years. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis that is responsible for the “high” that users experience. While much research has been conducted on the effects of THC on the brain, its relationship with dopamine is a topic that has gained significant interest among scientists and cannabis enthusiasts alike. In this article, we will explore the link between THC and dopamine, including how THC affects dopamine levels in the brain, the potential benefits and drawbacks of this interaction, and what implications this may have for cannabis users.
What is dopamine?
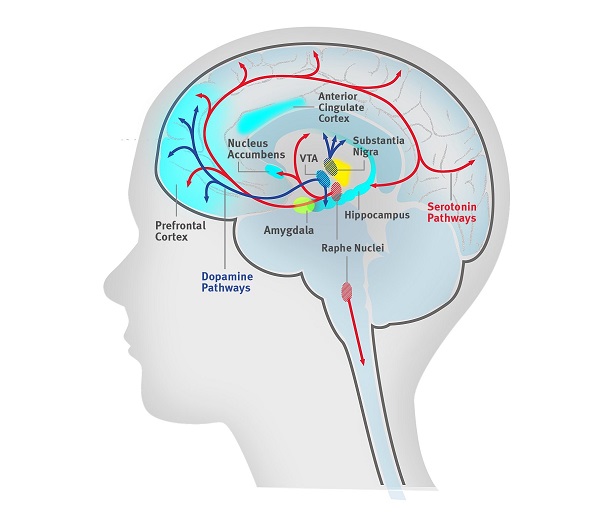
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter, a type of chemical messenger that is produced and released by nerve cells in the brain. It plays a crucial role in a wide range of physiological and psychological functions, including movement, motivation, reward, attention, learning, and memory.
Dopamine is synthesized from the amino acid tyrosine in several regions of the brain, including the substantia nigra, the hypothalamus, and the ventral tegmental area (VTA). Once produced, dopamine is stored in vesicles in the nerve cell terminals until it is released into the synaptic cleft, the small gap between nerve cells, in response to an electrical signal.
Dopamine then binds to receptors on the surface of neighboring nerve cells, triggering a series of biochemical events that ultimately result in the transmission of nerve impulses. The specific effects of dopamine on the brain depend on which receptor subtypes it binds to and where in the brain it is released.
One of the best-known functions of dopamine is its role in the brain’s reward system. When we experience something pleasurable, such as eating a delicious meal or receiving a compliment, dopamine is released in the brain, and we feel a sense of pleasure or satisfaction. This positive reinforcement can encourage us to repeat the behavior, reinforcing learning and memory processes.
However, dopamine is also involved in other functions beyond reward processing. For example, it plays a critical role in movement regulation, with low dopamine levels in the substantia nigra being associated with Parkinson’s disease. Dopamine is also involved in attention and focus, with medications that increase dopamine levels being used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Abnormal dopamine levels have been linked to a variety of neurological and psychiatric disorders. Low dopamine levels have been associated with depression, whereas high levels of dopamine in certain brain regions have been implicated in schizophrenia and addiction.
Overall, dopamine is a complex and multifaceted neurotransmitter that plays a vital role in many aspects of our brain function and behavior.
Does marijuana change dopamine levels in the brain?

Marijuana can change dopamine levels in the brain. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound in marijuana, interacts with the brain’s endocannabinoid system, which is involved in regulating neurotransmitters such as dopamine.
Research has shown that acute THC administration can increase dopamine release in several regions of the brain, including the striatum and prefrontal cortex. This increase in dopamine release is thought to be responsible for some of the rewarding effects of marijuana, as well as its potential for abuse and addiction.
However, chronic marijuana use may have the opposite effect on dopamine levels. Studies have suggested that chronic marijuana use can decrease dopamine release in certain regions of the brain, including the striatum and nucleus accumbens. This decrease in dopamine release is thought to be a consequence of downregulation of cannabinoid receptors in the brain, which can occur with repeated exposure to THC.
The effects of marijuana on dopamine levels may have important implications for both recreational and medicinal use of the drug. For example, the increased dopamine release associated with acute marijuana use may contribute to the drug’s potential for abuse and dependence, as well as its potential therapeutic effects for certain conditions such as chronic pain or nausea. However, the long-term effects of chronic marijuana use on dopamine levels may be associated with negative consequences such as decreased motivation and cognitive impairment.
It’s worth noting that the relationship between marijuana and dopamine is complex, and more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and implications of this interaction. However, it is clear that marijuana can affect dopamine levels in the brain, and that these effects may have important implications for both recreational and medicinal use of the drug.
CBD vs. THC

CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) are two of the most well-known compounds found in the cannabis plant. While they both interact with the endocannabinoid system in the body, they have different effects and uses.
THC is the primary psychoactive compound in marijuana, meaning it is responsible for the “high” or intoxicating effects associated with marijuana use. THC binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain, increasing dopamine release and altering perception, mood, and cognition. It is also used for medicinal purposes, such as pain relief, nausea, and muscle spasms.
CBD, on the other hand, is not psychoactive and does not produce the same intoxicating effects as THC. CBD does interact with the endocannabinoid system, but it does so differently than THC. Rather than binding directly to cannabinoid receptors in the brain, CBD can modulate the activity of these receptors, leading to a variety of effects throughout the body. CBD has been studied for its potential therapeutic effects, including anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, and antipsychotic properties.
In terms of legality, THC is classified as a Schedule I controlled substance under U.S. federal law, meaning it is considered to have a high potential for abuse and no accepted medical use. However, some states have legalized marijuana for both recreational and medicinal use. CBD, on the other hand, was legalized at the federal level in the United States with the passage of the 2018 Farm Bill, as long as it is derived from hemp and contains less than 0.3% THC.
Overall, CBD and THC have different effects and uses, and it’s important to understand these differences when considering the use of cannabis-derived products. It’s also important to note that the use of both CBD and THC can have potential risks and side effects, and individuals should consult with a healthcare professional before using these substances.
What happens when dopamine levels rise due to the effects of THC?
When dopamine levels rise due to the effects of THC, it can produce a number of psychological and physiological effects. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in reward and pleasure-seeking behaviors. When dopamine levels rise, it can produce feelings of euphoria, relaxation, and contentment. This is why THC is often associated with feelings of “high” or “buzzed”.
The increase in dopamine release caused by THC is thought to be responsible for some of the rewarding effects of marijuana, such as the relaxation and euphoria experienced by users. However, the long-term effects of chronic marijuana use on dopamine levels may be associated with negative consequences such as decreased motivation and cognitive impairment.
It’s worth noting that the effects of THC on dopamine levels may vary depending on the individual, as well as the dosage and method of administration of the drug. Additionally, while dopamine plays a key role in the rewarding effects of THC, other neurotransmitters such as serotonin and norepinephrine may also be involved in producing the overall effects of marijuana use.
Overall, while the increase in dopamine release caused by THC can produce feelings of euphoria and relaxation, it is important to understand the potential risks and side effects associated with marijuana use, particularly with chronic use.
Heavy cannabis use lowers dopamine levels
Studies have suggested that heavy cannabis use may lead to a decrease in dopamine release in certain regions of the brain. Chronic exposure to THC, the primary psychoactive compound in marijuana, can lead to downregulation of cannabinoid receptors in the brain, which can result in a decrease in dopamine release.
One study published in the journal Neuropsychopharmacology found that heavy cannabis users had significantly lower dopamine release in the striatum compared to non-users. The study also found that the decrease in dopamine release was associated with deficits in attention and working memory.
Another study published in the journal Biological Psychiatry found that chronic cannabis users had lower dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens, a region of the brain involved in reward processing and motivation, compared to non-users. The study also found that the decrease in dopamine release was associated with decreased motivation and reduced reward sensitivity.
While the long-term effects of chronic cannabis use on dopamine levels are still not fully understood, these studies suggest that heavy cannabis use may have negative consequences on dopamine release, which may be associated with decreased motivation, cognitive impairment, and other negative outcomes.
It is important to note, however, that the relationship between cannabis use and dopamine levels is complex, and the effects may vary depending on the individual, as well as the dosage and method of administration of the drug. More research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and implications of the interaction between cannabis and dopamine.
Treatment for marijuana use disorder

Treatment for marijuana use disorder typically involves a combination of behavioral therapies and medications. The specific treatment approach will depend on the severity of the disorder, as well as the individual’s needs and preferences. Here are some common treatment options:
- Behavioral therapies: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a commonly used therapy for marijuana use disorder. CBT focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors related to drug use, and developing new coping strategies. Motivational interviewing and contingency management are other behavioral therapies that may be used to help individuals with marijuana use disorder.
- Medications: Currently, there are no FDA-approved medications for the treatment of marijuana use disorder. However, some medications that are used to treat other substance use disorders may be helpful for individuals with marijuana use disorder. For example, bupropion, an antidepressant, may help reduce cravings for marijuana. Naltrexone, which is used to treat opioid and alcohol use disorders, may also be helpful in reducing marijuana use.
- Support groups: Support groups, such as Marijuana Anonymous or SMART Recovery, can provide a supportive environment for individuals struggling with marijuana use disorder. These groups offer peer support, education, and resources for maintaining sobriety.
- Residential treatment: For individuals with severe marijuana use disorder, a residential treatment program may be recommended. Residential treatment programs provide 24-hour care and support, as well as intensive therapy and counseling.
It is important to note that treatment for marijuana use disorder is not a one-size-fits-all approach, and the best treatment approach will depend on the individual’s unique needs and circumstances. A healthcare professional can help determine the most appropriate treatment plan for an individual with marijuana use disorder.
Conclusion
The relationship between THC and dopamine is complex and has important implications for understanding the effects of cannabis on the brain and behavior. THC is known to increase dopamine release, which can lead to feelings of euphoria and reward. However, chronic and heavy cannabis use can lead to a decrease in dopamine release, which can result in negative effects on motivation, attention, and working memory. The effects of THC on dopamine release may also vary depending on the individual and the method of administration of the drug. Further research is needed to better understand the mechanisms underlying the relationship between THC and dopamine and to develop effective treatments for individuals struggling with marijuana use disorder.