Cannabis, also known as marijuana, has been used for medicinal purposes for thousands of years. In recent years, the use of cannabis for medical purposes has become more widespread, particularly with the legalization of medical marijuana in several countries. One of the most commonly discussed aspects of cannabis is its chemical compounds, specifically tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). However, there is another lesser-known compound in cannabis that is beginning to gain attention: hexahydrocannabinol (HHC). In this article, we will explore the differences between HHC and THC, including their chemical structures, effects on the body, and potential medical uses.
What is HHC?

Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is a naturally occurring chemical compound found in the cannabis plant. It is structurally similar to tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive compound in cannabis that is responsible for its mind-altering effects. However, HHC has a slightly different chemical structure than THC, which may result in different effects on the body.
HHC was discovered in the 1940s by chemist Roger Adams. He created HHC by adding hydrogen to the THC molecule and altering its physical properties. The process, called hydrogenation, is first described in a 1947 patent document.
Hydrogenation modifies the structure of delta 9 THC by replacing a double bond with two hydrogen atoms, which changes its molecular weight and also makes it more stable. According to Mark Scialdone, a chemist and BR Brands Chief Science Officer, hydrogenation improves “stability and resistance to thermo-oxidative breakdown”—which means HHC has a longer shelf life and is less prone to damage caused by UV light and heat.
Benefits of HHC
Hexahydrocannabinol is a relatively new and understudied chemical compound found in cannabis that is believed to offer several potential health benefits. While more research is needed to fully understand the effects of HHC on the body, early studies suggest that it may have therapeutic properties in the following areas:
- Appetite Stimulation: HHC has been found to act as an appetite stimulant in animal studies, promoting weight gain and increasing food intake. This could make it a potential treatment option for individuals with conditions that cause a loss of appetite, such as cancer or HIV/AIDS.
- Pain Management: HHC has been found to have analgesic, or pain-relieving, properties. In one study, HHC was found to be more effective than THC at reducing pain in mice, indicating that it may have potential as a pain management tool.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: HHC has been found to reduce inflammation in animal studies, which could make it a useful therapeutic agent for individuals with inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease.
- Anti-Anxiety Effects: While more research is needed, preliminary studies suggest that HHC may have anti-anxiety effects. In one study conducted on mice, HHC was found to reduce anxiety-like behavior.
- Anti-Tumor Properties: Some studies suggest that HHC may have anti-tumor properties. In one study conducted on mice, HHC was found to inhibit the growth of tumor cells, indicating that it may have potential as a cancer treatment.
While the potential benefits of HHC are promising, it is important to note that more research is needed to fully understand the effects of this compound on the body.
Potential side effects of HHC
As with any medication or supplement, it is important to be aware of the potential side effects of hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) before using it. While more research is needed to fully understand the effects of HHC on the body, early studies suggest that it may have some potential side effects, including:
- Impaired Cognition: HHC, like other cannabis compounds, may cause impairment in cognitive function, including short-term memory, attention, and decision-making.
- Dizziness: HHC may cause dizziness or lightheadedness, especially at higher doses.
- Changes in Blood Pressure and Heart Rate: HHC may cause changes in blood pressure and heart rate, which could be problematic for individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
- Respiratory Issues: If HHC is consumed through smoking or vaping, it may cause respiratory issues, such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
- Dry Mouth: HHC, like other cannabis compounds, may cause dry mouth or “cottonmouth,” which can be alleviated by drinking water or other fluids.
- Psychiatric Effects: While more research is needed, preliminary studies suggest that HHC may have psychiatric effects, including anxiety and paranoia.
- Addiction: HHC, like other cannabis compounds, may have the potential to be addictive. Individuals with a history of substance abuse should exercise caution when using HHC or other cannabis-based therapies.
It is important to note that the potential side effects of HHC may vary depending on the dose and method of consumption. Additionally, not everyone who uses HHC will experience side effects. As with any medication or supplement, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before using HHC or any other cannabis-based therapy to understand potential risks and benefits.
Does HHC get you high?

Some experts argue that HHC produces the same effects as delta 8 THC, but it takes much more compound to make the same results. But those folks are in the minority, as most will note that HHC is much stronger than delta 8. According to those who have used it, HHC’s effects are very similar to THC. When using HHC, one may feel:
- Euphoria;
- Altered auditory perception;
- Altered visual perception;
- Altered cognition.
As for feeling relaxed, HHC feels very similar to delta 8. On the other hand, some users claim that they feel energetic and can think more clearly after using it.
HHC causes users to feel buzzed or high — more so than delta 8 but less than delta 9. So, with HHC, users typically have a potent or Delta 8 THC-like effect. That makes this an excellent cannabinoid for those looking for something substantial but not too strong — small doses that don’t overwhelm your senses. But even more than that, HHC can be used by those looking for more than just a buzz.
Although HHC will cause intoxication, the level of intoxication will be far less than delta-9 THC, which can be found in marijuana.
How potent is HHC?
Some conflicting reports are out there, with some so-called experts saying it is less potent than delta 8 and others noting it is a potent cannabinoid. Many early reports about HHC stated that it was a mild cannabinoid, only about half as powerful as delta 8 THC. However, it turns out that they were incorrect. The truth of the latter is that HHC is one of the more potent compounds on the legal market today.
Will HHC trigger a drug test?

Many alternative forms of THC, such as delta 8 THC and delta 10 THC, will appear on urine or blood tests for THC if they consume enough of them in sufficient amounts. But HHC does not.
Although, at this time, the evidence supporting this claim is mainly anecdotal, preliminary research suggests that HHC doesn’t metabolize into 11-hydroxy-THC. This primary THC metabolite may cause a positive test result to appear.
Still, it’s always best to abstain from using anything before a drug test, as nothing is guaranteed.
What is the proper dose for HHC?
Finding the proper dose of HHC can be difficult. Doing so depends significantly on the individual and their tolerance to certain cannabinoids. If a user has a high tolerance, they may wish to start with a higher dose of HHC. Conversely, those with a lower tolerance to cannabis may want to try a lower amount to start.
Remember that HHC sits between Delta 8 and Delta 9 regarding potency. In this case, the following dosages are usually distinguished:
- Low – 10-20mg.
- Moderate – 20-50mg.
- High – 50-100mg.
Individuals who are interested in using HHC for therapeutic purposes should consult with a healthcare professional to discuss potential risks and benefits and to determine the appropriate dosage for their individual needs.
Is HHC legal?
The legality of HHC varies depending on the jurisdiction. In the United States, the legal status of HHC is complicated, but most experts agree it’s legal under current federal regulations (2018 Farm Bill) — as long as it’s derived from hemp and contains no more than 0.3% THC by dried weight. However, the legal status of HHC may be different at the state or local level, and laws regarding the production, sale, and use of HHC may vary.
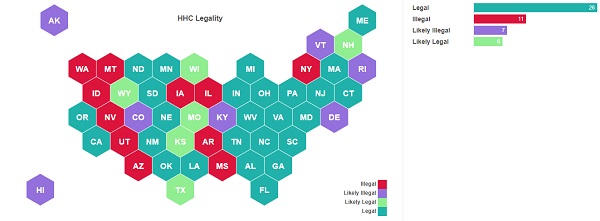
Therefore, individuals who choose to use HHC or other cannabinoids should be aware of the legal status in their jurisdiction and should take appropriate precautions to avoid legal issues.
What is THC?

THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is a chemical compound found in the cannabis plant. It is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, responsible for the “high” that is associated with the plant. THC is one of over 100 cannabinoids found in cannabis, and it is the most well-known and extensively studied.
Benefits of THC
THC has been studied for its potential therapeutic benefits and has been found to have a variety of positive effects on the body. Some of the potential benefits of THC include:
- Pain relief: THC has been found to be effective in relieving both acute and chronic pain. It works by binding to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and nervous system, which can help reduce pain perception.
- Reducing inflammation: THC has been found to have anti-inflammatory effects, which can be helpful for treating conditions such as arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and other inflammatory conditions.
- Reducing nausea and vomiting: THC has been found to be effective in reducing nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy and other medical treatments.
- Stimulating appetite: THC can increase appetite and may be helpful for individuals who have a loss of appetite due to medical conditions such as HIV/AIDS or cancer.
- Improving sleep: THC can help improve sleep by reducing the time it takes to fall asleep and increasing the duration of sleep.
- Reducing anxiety and depression: While THC can sometimes cause anxiety or paranoia, it has also been found to have anti-anxiety and antidepressant effects in some individuals.
- Reducing seizures: THC has been found to have anticonvulsant properties and may be helpful for individuals with epilepsy or other seizure disorders.
It is important to note that the therapeutic effects of THC can vary depending on the individual’s health status, the method of consumption, and other factors.
Side effects of THC
THC can have a range of potential side effects, especially when consumed in high doses or by individuals who are sensitive to its effects. Some of the most common side effects of THC include:
- Impaired coordination: THC can affect motor coordination and impair an individual’s ability to drive or operate heavy machinery.
- Cognitive impairment: THC can affect cognitive function, including memory, attention, and concentration.
- Increased heart rate: THC can cause an increase in heart rate, which can be dangerous for individuals with pre-existing heart conditions.
- Dry mouth and eyes: THC can cause dry mouth and eyes, which can be uncomfortable and lead to an increased risk of dental problems.
- Anxiety and paranoia: In some individuals, THC can cause feelings of anxiety, paranoia, or panic.
- Hallucinations: THC can cause hallucinations in some individuals, particularly when consumed in high doses.
- Addiction and dependence: THC has the potential to be addictive and can lead to dependence in some individuals.
- Respiratory problems: Smoking THC can lead to respiratory problems, such as bronchitis or chronic coughing.
It is important to note that the effects of THC can vary depending on the individual’s tolerance and metabolism, the method of consumption, and the dose. Some individuals may be more sensitive to THC than others and may experience more severe side effects.
Does THC get you high?

THC is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis and is responsible for the “high” or euphoric effects that are typically associated with cannabis use. When THC is consumed, it binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and central nervous system, which can lead to a range of effects, including a sense of relaxation, altered perception of time, and changes in mood and appetite.
The intensity of the “high” can vary depending on the individual’s tolerance and metabolism, the method of consumption, and the dose.
How potent is THC?
The potency of THC can vary depending on the strain of cannabis and the method of consumption. In general, THC potency is measured as a percentage of the total weight of the cannabis product.
For example, in dried cannabis flower, THC potency can range from less than 5% to more than 30%. Some high-potency strains can even have THC levels above 35%.
In cannabis concentrates, such as oils or wax, THC potency can be even higher, with some products containing upwards of 90% THC.
The potency of THC can also vary depending on the method of consumption. When cannabis is smoked or vaporized, the effects of THC are usually felt within minutes and can last for a few hours. When cannabis is consumed orally, such as in edibles, the effects can take longer to onset and may last for several hours.
It is important to note that higher potency does not necessarily mean a better or more enjoyable experience. THC potency should be considered along with other factors, such as the desired effects and potential risks and side effects. Individuals who are new to cannabis or who are using it for therapeutic purposes should start with a low dose and gradually increase as needed. It is also important to use cannabis responsibly and in compliance with local laws and regulations.
Is THC legal?
The legality of THC depends on the country and jurisdiction. In some countries and states, THC is legal for medical and/or recreational use, while in others it remains illegal.
In the United States, THC is still considered a Schedule I drug under federal law, which means it is illegal at the federal level. However, many states have legalized cannabis for medical and/or recreational use, and the legality of THC varies by state.
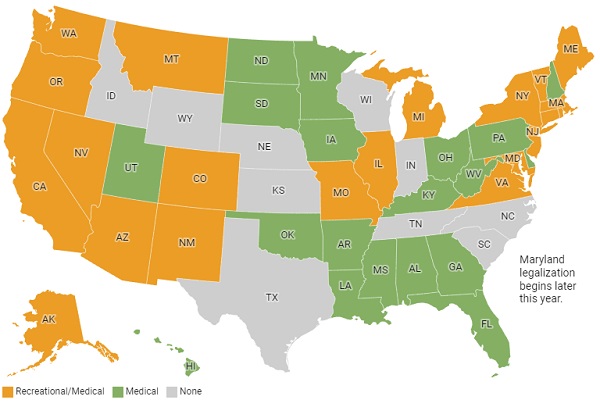
In countries where cannabis is legal, THC may be legal for medical and/or recreational use. However, it is important to note that even in places where cannabis is legal, there may be restrictions on THC potency, age limits for use, and regulations around the sale and consumption of cannabis products.
It is important to check local laws and regulations regarding THC and cannabis use, and to use cannabis responsibly and in compliance with local laws.
HHC vs THC

To better understand the potency of THC and HHC, we need to look at their chemical structures. The body binds to THC more tightly than HHC, making it a more complex cannabinoid. There are therapeutic benefits for both THC and HHC. However, THC has been extensively studied and is widely known to be comparable to a THC high, if not stronger. Users claim that HHC has a “cleaner” high than marijuana, with no hangovers. It is estimated that THC is three times stronger than traditional marijuana and up to five times stronger than HHC. THC may take several hours to kick in, but the effects are much more intense and can last up to six hours.
On the other hand, Delta 8 THC is the cannabinoid to beat these days. It was the first all-natural, hemp-derived cannabinoid with a buzz to hit the market. The best part about Delta 8 THC is that it’s federally legal, thanks to the Farm Bill, allowing users to enjoy the buzz without interference from anyone.
But HHC is something altogether different. It’s a cannabinoid with about twice the potency of Delta 8, making it the perfect product for anyone looking for something stronger.
As for comparing HHC to Delta 10, it’s two cannabinoids in different stratospheres. Delta 10 THC is a hemp-based cannabinoid made for people who like to move and shake. It’s for those who need to keep going to get things done. People who take Delta 10 products will find themselves energized and focused, with a burst of creative energy flowing through them. It’s the opposite of HHC.
Final thought
THC and HHC are two cannabinoids with different chemical structures and effects on the body. While THC is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis and is responsible for the “high” or euphoric effects, HHC is a relatively new cannabinoid that may have different potency and duration of effects compared to THC.
Both THC and HHC have potential therapeutic benefits, including pain relief, anti-inflammatory properties, and appetite stimulation. However, it is important to note that research on HHC is still limited, and its therapeutic benefits and potential risks and side effects are not yet fully understood.
Individuals who are considering using THC or HHC should consult with a healthcare professional and use cannabis products responsibly and in compliance with local laws and regulations.