We know you’re almost done learning the nuances of the stellar cannabinoids THC and CBD and how they affect your buzz; you know how they interact with other cannabis-derived compounds called terpenes, and you may have studied the much-discussed entourage effect. Endocannabinoid system? No problem. But now we’re going to break that down with another compound: THCA. Cannabis plants produce over 100 different cannabinoids, each of which influences how you are affected by smoking, vaping, edible or local products. While you may not realize it, THCA is part of the plant and it’s time to learn more about it.
What is THCA?
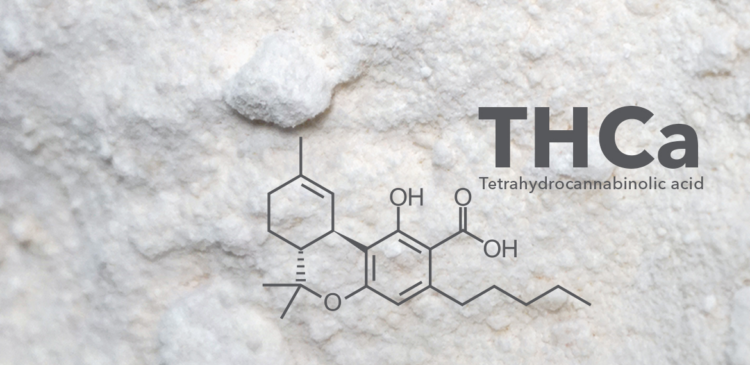
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, or THCA, is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in raw and unheated cannabis plants. The acidic form of THC, THCA, does not cause a high. The chemical structures of both cannabinoids are similar, but their functions are different.
THCA is derived from CBGA, also known as the “mother of all cannabinoids”. CBGA is produced by the cannabis plant as it matures. Because THCA has an extra molecular carboxyl ring, it cannot bind to brain receptors to produce the euphoric high associated with THC.
While you may not get high directly from THCA, the compound still has many positive benefits that impact your marijuana experience. And, of course, THCC is best known for converting to THC when exposed to heat. In other words, THCC is not a psychoactive substance, but allows the creation of THC, which is marijuana’s main psychoactive compound.
THC vs. THCA
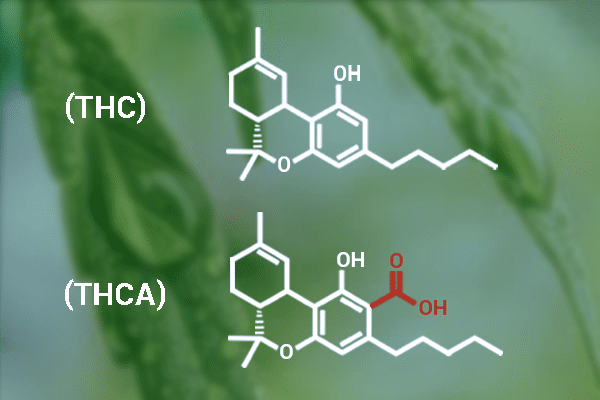
The biggest difference between THCA and THC is that THCA does not have the intoxicating effect that THC does. However, THCA must be heated to create THC by smoking, vaping, dipping, or cooking. This transformation changes the molecular structure of THCA by removing the carboxyl ring. It also helps THC bind to CB1 receptors in our body.
Effects-wise, THCA and THC overlap in some areas. Both have potential to treat nausea, but THCA shows far more promise for addressing inflammation. On the flip side, because THCA isn’t intoxicating, some may find it less effective for sleep than activated THC. And while THC isn’t recommended for seizure disorders, THCA may show some promise in addressing those conditions.
Is a higher level THCA or THC better?
All states with a medical or recreational cannabis program require brands and cannabis operators to test products in a third-party lab to ensure they are suitable and safe before they can be sold to the public. THCA and THC levels will help you determine how effective a product is and what kind of experience you expect.
While it may seem like you need a high level of THC, direct heating of the THC can burn off some of the cannabinoid content and make you want more.
If you’re not looking for edibles, you want high THCA values, not necessarily THC; that THCA represents the full potential of whatever you’re about to smoke, smear or vape because it converts to THC. Whether you are looking for flower, vape cartridges or concentrates, you need to check the THCA number. All of these products require decarboxylation, i.e. activation by heat, to produce an effect.
Is THCA the same as delta-8 or delta-9?
THCA is the acidic form of delta-9 THC, the best-known intoxicating compound in cannabis.
Delta-8 THC has the same number of atoms as delta-9, but their arrangement is different and this arrangement affects its effects. This is how companies were able to legally manufacture delta-8 products from hemp plants, which are required by law to contain less than 0.3% delta-9 THC.
Delta-8 is also derived from THCA, called delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinic acid, but there are few studies to understand how it compares to THCA. Also, both delta-8 and delta-9 THC have some degree of intoxicating effect when consumed. They are not in acidic form like THCA.
What are THCA’s effects and benefits?
Raw cannabis does not produce a high if consumed without decarbing first. However, consuming raw cannabis for its THCA content, through juicing, for example, or taking a THCA-based tincture or edible, provides some of the same benefits as activated THC without intoxication.
Some anecdotal accounts believe THCA produces some effect, but THCA’s molecular structure prevents it from binding with CB receptors in our bodies’ endocannabinoid systems.
There is not enough data to indicate that THCA does not provide pain relief to users in the same way that THC does, although it still interacts with our receptors in a more peripheral way. Research has shown that it also has potential neuroprotective properties that may help slow down and prevent neurodegenerative diseases such as Huntington’s disease. It can also help treat conditions like colitis and IBS. Preliminary evidence suggests that THCA may help with seizure disorders.
How to use THCA
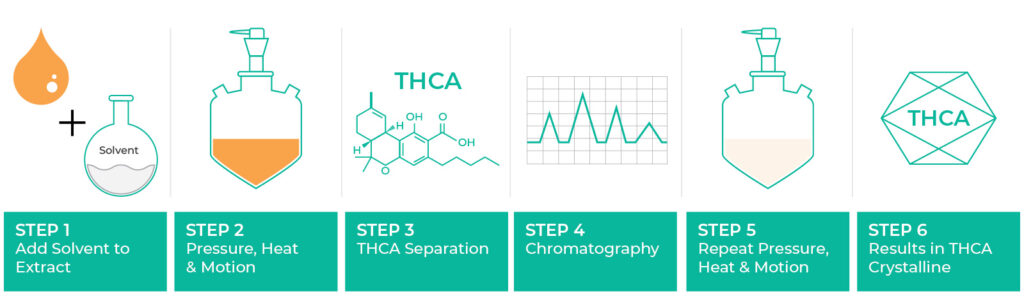
Many smokers and patients use THCA converted to THC every day by smoking, wiping, vaping and ingesting a form of weed to get high or eliminate their symptoms. In these cases, THCA is more of a conduit for the benefits of THC. But more and more brands are paying attention to the benefits of THCA for self use.
One popular and affordable way to use THCA is through the consumption of raw cannabis. You can literally just eat it, but many people prefer to include it in their juicing routine for greater potency and flavor. Many companies also make THCA tinctures and topical products such as vitamins or post-workout massages.
How to activate THCA
The good news is, activating THCA is as easy as packing, lighting, and inhaling! Stoners, patients, and casual users activate THCC every day when they smoke weed, swipe, smoke a vape pen, and do any other heat-related activity.
You can also decarboxylate cannabis for foods, tinctures, and topical applications. We have several ways to do this, but it all comes down to exposing the cannabis flower to temperatures around 200-245ºF for 30-40 minutes in a conventional oven. Anything above 300º will burn the cannabinoid content, as will cooking too long.
Should you smoke or dab THCA?
Yes, but THCA won’t be around for long. In fact, you need to expose the cannabis product to heat in some way or else you won’t get a high or any other benefits such as pain relief, appetite stimulation, and nausea reduction. Upon contact with heat, such as your lighter, vape pen battery, or quartz nail, THCA will immediately begin to convert to THC. So when you smoke a joint, pack a bowl, hit a bong, rip open a Volcano bag, flick your Puffco, etc., etc., you are inhaling mostly THC.
Does THCA show up on a drug test?
Yes, both THC and THCA will show up as positive on a drug test. It is impossible to fully decarboxylate the full THCA content of the weed you smoke or dabs you take into THC, so you likely are absorbing THCA as well; the same goes for some types of rosin- and/or hash-based gummies due to the lack of cannabinoid isolation, though due to required lab testing, it’s less likely.
How do you dose THCA
As a cannabinoid with many potentially beneficial effects, THCA is certainly worth exploring. In some studies, THCA has shown significant health benefits at lower doses than other cannabinoids, which means that consumers can use less product while still getting more relief. THCA dosage should be 10 to 100 times lower than THC dosage, according to some sources. In preclinical studies, full spectrum extracts of THCA are shown to be 10 times more potent than isolates.
Research on THCA and how to dose it is still in its infancy, so we don’t yet have definitive recommendations on how much to take.
THCA should be taken according to the same rule of thumb as other cannabinoids: start small and increase the dosage until you feel comfortable. The THCA product most likely comes with instructions on how to use it. Make sure you follow the dosage recommendations on your product’s packaging, or better yet, start with a slightly lower recommended dose.
It is important to remember that cannabinoid dosage is not an exact science as it depends on many factors such as weight, age, metabolism and tolerance so only you can determine what is right for you.
Summary
So what is THCA? Although widely regarded as a precursor to THC, the compound itself has much more to offer than the potential to be psychoactive. In some studies, THCA has shown promising results in many scientific areas such as anti-inflammatory effects, neuroprotection, and obesity prevention.
When taking THCA, it is important to understand that any form of heat will effectively convert the compound into THC, which will leave you high despite its non-psychoactive nature. If you want to convert THCA to THC to create a psychoactive compound feel free to use heat. If you want the non-psychoactive effects of a compound, keep it away from heat sources (including the sun).
So, you’re done! A complete, comprehensive explanation of the wonderful and sometimes confusing nature of THCA. Now that you have this information, we hope you can make informed decisions about your cannabinoid products in the future.
FAQ
Is THCA Legal?
In terms of legality, THCA is quite complicated. Federally, the compound has not been classified as a controlled substance. Possession of THCA could get you into legal trouble, however, if you attempt to decarb raw cannabis. As soon as THCA is decarbed, it becomes THC, the psychoactive compound in cannabis that remains illegal at the federal level. Additionally, the DEA could consider THCA an analog of THC and press charges under the Federal Analog Act.
The Farm Act is another important legal document affecting the legality of THCA. The Agricultural Act, or the Agricultural Improvement Act as it is also called, distinguishes legal hemp from illegal marijuana based on the delta 9 content of each plant. Cannabis containing 0.3% THC or less is classified as hemp, and cannabis containing more than 0.3% THC is classified as marijuana.
Under the Farm Act, a bud with 20% THCA and only 0.2% THC qualifies as cannabis and therefore also legal under federal law. Despite the federal government’s ruling, some states have taken steps to restrict or ban hemp-derived cannabinoids. There are also some states that have enacted their own medical and recreational marijuana laws that differ from those of the federal government. Thus, summing up, it is important to understand that the rule of law becomes more complex at the state level.
While the THCA flower is completely legal in some states, such as North Carolina, which does not currently use a “total THC” standard for hemp in any of its regulations, it is restricted in other states, such as Oregon. In states like Pennsylvania, where authorized hemp processors can only use cannabis material that has passed a general THC test, determining whether THC is legal or not can be a little tricky because retailers of finished hemp products don’t need hemp permits. and therefore the general THC Requirement does not apply in their case.
While THCA appears to be legal when it comes from hemp containing less than 0.3% THC, and dubiously legal when it comes from marijuana, determining its status under state law is much more complicated than understanding its blanket legality under federal law. This can lead to confusion and misunderstanding of hemp laws at a state level, which is why it is important that you research your state’s hemp laws on your own to understand where your state stands on this compound.
Where can I find THCA?
Until recently, few products have taken advantage of the many benefits of THCA, but many brands now produce THCA-focused products for oral and topical use.
While both medical marijuana and recreational dispensaries can legally sell THCA-based or infused products, you’re more likely to find them in a store that has more emphasis on medicinal products. And keep in mind, you won’t burn them.