Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver cells. It is a common health issue affecting millions of people worldwide, and if left untreated, it can lead to more severe liver problems, such as cirrhosis and liver failure. In recent years, there has been growing interest in the potential use of cannabis-derived compounds, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), for treating various medical conditions. However, there is limited research on the effects of THC on fatty liver disease, and the available studies have yielded conflicting results. This article aims to explore the current evidence regarding the relationship between THC and fatty liver disease and discuss its potential therapeutic implications.
Fatty Liver Disease
Causes of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver cells. It is a common health problem affecting millions of people worldwide. There are two main types of fatty liver disease: alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). AFLD is caused by excessive alcohol consumption, while NAFLD is not related to alcohol intake and is typically associated with metabolic disorders such as obesity, diabetes, and high blood pressure.
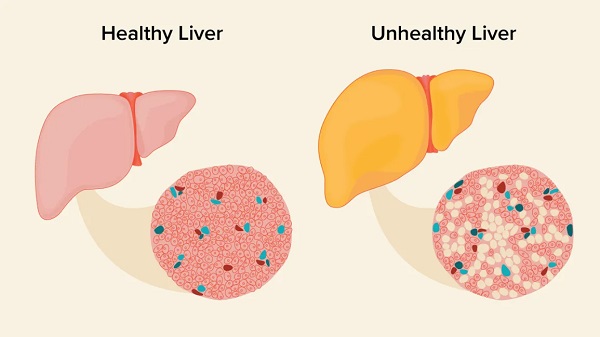
NAFLD is considered to be one of the most common liver diseases worldwide, affecting approximately 25% of the global population. The exact cause of NAFLD is not well understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It occurs when the liver produces too much fat or is unable to metabolize fat efficiently, leading to the accumulation of fat in liver cells.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
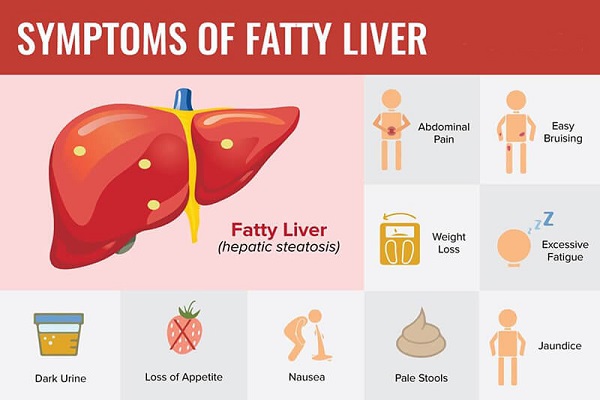
Fatty liver disease is often asymptomatic, meaning that many people with the condition do not experience any noticeable symptoms. However, some common symptoms of fatty liver disease include fatigue, weakness, and abdominal pain. Diagnosis typically involves blood tests, imaging tests, and liver biopsy.
Consequences of Fatty Liver Disease
The potential consequences of fatty liver disease can be serious, particularly if the condition is left untreated. In some cases, the liver may become inflamed, a condition known as steatohepatitis. This can lead to liver fibrosis, or the buildup of scar tissue in the liver. As fibrosis progresses, it can lead to cirrhosis, a condition in which the liver is permanently damaged and cannot function properly.
In addition to liver damage, fatty liver disease can also increase the risk of other health problems. For example, people with fatty liver disease may be at increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. There is also evidence to suggest that fatty liver disease may increase the risk of liver cancer.
Treatment and risk factors
The treatment of fatty liver disease depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. In cases of AFLD, the primary treatment is to stop drinking alcohol. In cases of NAFLD, treatment typically involves lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss, exercise, and a healthy diet. In some cases, medications may also be prescribed to help reduce inflammation and improve liver function.
Here are some of the risk factors for developing fatty liver disease:
- Obesity or being overweight;
- Type 2 diabetes;
- High blood pressure;
- High levels of triglycerides in the blood;
- Metabolic syndrome;
- Rapid weight loss;
- Malnutrition;
- Certain medications.
Effect of THC on fatty liver disease
Recent studies have suggested that THC, the main psychoactive compound found in cannabis, may have potential therapeutic effects for treating fatty liver disease. THC is known to interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which plays a key role in regulating metabolism and inflammation, two processes that are closely linked to the development of fatty liver disease.
Positive Effects of THC on Fatty Liver Disease
One study published in the Journal of Hepatology found that treatment with THC reduced liver steatosis (fat accumulation) and inflammation in mice with diet-induced fatty liver disease. The study also found that THC improved insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance, two factors that are often impaired in people with fatty liver disease. These findings suggest that THC may have potential as a treatment for fatty liver disease.
Another study published in the journal Liver International found that THC treatment improved liver function and reduced liver injury in mice with alcohol-induced fatty liver disease. The study also found that THC reduced oxidative stress and inflammation in the liver, which are two key factors that contribute to the development of liver damage in people with fatty liver disease.
While these studies suggest that THC may have therapeutic potential for treating fatty liver disease, more research is needed to determine its safety and efficacy in humans. It is also important to note that the use of cannabis for medical purposes should always be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Negative Effects of THC on Fatty Liver Disease
While there is some evidence that THC may have potential therapeutic effects for treating fatty liver disease, there are also potential negative effects of THC use on the liver, particularly when used excessively or in combination with other substances.
One study published in the journal Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology found that regular cannabis use was associated with an increased risk of developing liver fibrosis, a condition in which scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue. The study also found that cannabis use was associated with more severe liver fibrosis in people with hepatitis C, a viral infection that can cause liver damage.
Another study published in the journal Drug and Alcohol Dependence found that cannabis use was associated with an increased risk of liver disease progression in people with hepatitis C. The study found that cannabis use was associated with a higher likelihood of developing cirrhosis, a severe form of liver disease that can lead to liver failure.
It is important to note that these studies do not necessarily prove that cannabis use directly causes liver damage, as there may be other factors that contribute to both cannabis use and liver disease. However, they do suggest that excessive cannabis use may be a risk factor for liver disease and that people with existing liver problems should use cannabis with caution.
Potential Mechanisms of Action of THC on Fatty Liver Disease
The potential mechanisms of action of THC on fatty liver disease are still being studied, but several possible pathways have been proposed. THC is known to interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which plays a key role in regulating metabolism and inflammation, two processes that are closely linked to the development of fatty liver disease.
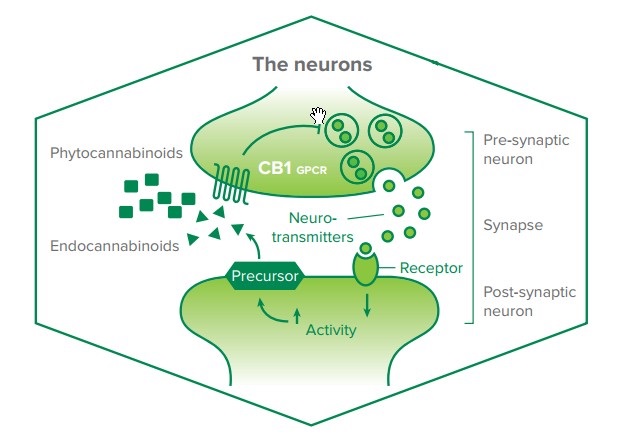
One potential mechanism is through the activation of the CB1 receptor, which is found in high levels in the liver and is known to play a role in regulating metabolism and inflammation. THC has been shown to activate the CB1 receptor, which may help to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation in the liver, both of which are important factors in the development of fatty liver disease.
Another potential mechanism is through the regulation of lipid metabolism. THC has been shown to reduce the accumulation of fat in the liver by promoting the breakdown of triglycerides, a type of fat that is stored in the liver. This may help to reduce the risk of developing fatty liver disease.
THC has also been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, which may help to reduce inflammation in the liver and prevent the progression of fatty liver disease. THC has been shown to reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are proteins that are involved in the inflammatory response.
It is important to note that the mechanisms of action of THC on fatty liver disease are still not fully understood, and more research is needed to determine the exact pathways involved.
Implications for Medical Use: Potential Benefits and Risks
The potential medical use of THC in the treatment of fatty liver disease has generated interest among medical researchers and clinicians, but it is important to consider both the potential benefits and risks associated with its use.
Potential Benefits
Several studies have suggested that THC may have therapeutic potential for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and liver fibrosis, by reducing liver fat accumulation and inflammation, improving insulin sensitivity, and reducing the risk of liver fibrosis. THC may also have anti-fibrotic effects, by reducing the accumulation of scar tissue in the liver and promoting the regeneration of healthy liver tissue. While the research is still in its early stages, these potential benefits suggest that THC could have a valuable role in the treatment of fatty liver disease.
Potential Risks
However, there are also potential risks associated with the use of THC, particularly when used over the long-term. These risks include cognitive impairment, addiction, and potential negative effects on mental health. There are also potential risks associated with the use of THC in combination with other medications or substances, particularly opioids or alcohol.
It is also important to note that the legal status of THC varies widely across different countries and jurisdictions, and the use of THC for medical purposes may not be legal in all areas. In addition, the quality and safety of THC products can vary widely, particularly in areas where regulation is limited.
Conclusion
The relationship between THC and fatty liver disease is complex and still not fully understood. While some studies suggest that THC may have potential benefits for reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the liver, other studies indicate that THC can exacerbate liver damage and promote the development of fatty liver disease. More research is needed to fully understand the potential risks and benefits of using THC for fatty liver disease.
It is important to note that the use of THC for medical purposes should always be done under the supervision of a healthcare professional. Patients with liver disease should be aware of the potential risks associated with THC use and should discuss the benefits and risks with their healthcare provider before using any cannabis-based products.
Overall, while the potential benefits of using THC for fatty liver disease are promising, more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms of action and potential risks associated with its use. As always, it is important to approach any medical treatment with caution and consult with a healthcare professional to ensure safe and effective use.