Marijuana, also known as cannabis, is a popular recreational drug that is consumed by millions of people worldwide. The main psychoactive ingredient in cannabis is delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is responsible for the drug’s characteristic effects on mood and perception. While THC is generally considered safe, there are concerns about its potential to interact with other drugs and cause adverse effects. One such concern is whether THC can cause serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when there is an excess of the neurotransmitter serotonin in the body. In this article, we will explore the relationship between THC and serotonin syndrome and examine the evidence behind this potential interaction.
What is serotonin?
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter, a chemical messenger that transmits signals between neurons in the brain and other parts of the body. It is also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT). Serotonin plays a key role in regulating many physiological and behavioral processes, including mood, appetite, sleep, and pain perception.
Serotonin is synthesized in the brain and other tissues from the amino acid tryptophan. It is then stored in vesicles within neurons and released when an action potential reaches the neuron. Once released, serotonin binds to specific receptors on the surface of neighboring neurons, transmitting a signal across the synapse.
In addition to its role in regulating mood and other physiological functions, serotonin is also involved in the regulation of many other processes, including blood clotting, immune function, and gastrointestinal motility.
Abnormalities in serotonin signaling have been implicated in several psychiatric and neurological disorders, including depression, anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and schizophrenia. Serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), a class of drugs that block the reuptake of serotonin, are commonly used to treat these disorders. However, excessive activation of serotonin receptors can lead to serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition that can occur when there is an excess of serotonin in the body.
Does cannabis increase serotonin?
The effects of cannabis on serotonin are complex and not fully understood. While some studies have suggested that cannabis use may increase levels of serotonin in the brain, others have found no significant changes in serotonin levels.
THC, the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, can interact with serotonin receptors in the brain. Specifically, THC has been found to bind to the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor, which is involved in mood regulation and the perception of sensory stimuli.
Does THC release serotonin?
In addition to its effects on serotonin receptors, THC may also indirectly affect serotonin levels through its interactions with other neurotransmitter systems. For example, THC has been shown to increase the release of dopamine, another neurotransmitter that can modulate serotonin release.
However, the effects of cannabis on serotonin levels and signaling are likely to be complex and context-dependent. The relationship between cannabis and serotonin is an active area of research, and further studies are needed to fully understand the effects of cannabis on serotonin signaling and its potential implications for health and disease.
Symptoms of serotonin syndrome: What are they?
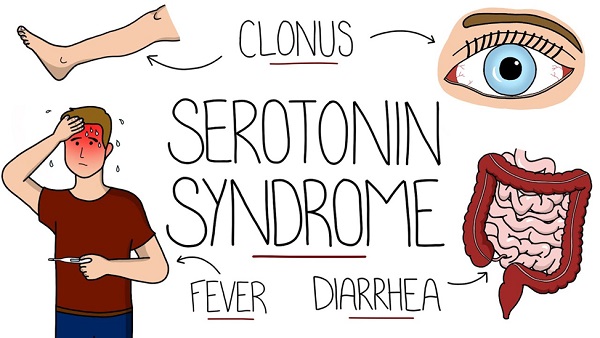
Serotonin syndrome is a potentially life-threatening condition that can occur when there is an excessive accumulation of serotonin in the body. When too much serotonin accumulates in the body, it can cause a range of symptoms, including:
- Mental changes: These may include agitation, confusion, disorientation, hallucinations, and anxiety. A person with serotonin syndrome may feel like they are in a state of constant nervousness or panic.
- Physical changes: Physical symptoms of serotonin syndrome can include rapid heart rate, high blood pressure, dilated pupils, and increased body temperature. These symptoms can be very dangerous and can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
- Muscular changes: Serotonin syndrome can cause muscle rigidity or stiffness, tremors, and twitching. In severe cases, the muscles can become so stiff that they may begin to break down, releasing toxins that can damage other organs.
- Gastrointestinal changes: Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are common symptoms of serotonin syndrome. These symptoms can lead to dehydration, which can further exacerbate other symptoms of the condition.
- Skin changes: People with serotonin syndrome may experience flushing of the skin. They may also experience sweating or shivering.
- Coordination changes: Serotonin syndrome can affect a person’s balance and coordination, making them more prone to falls and other accidents. In severe cases, the person may experience seizures or even slip into a coma.
The symptoms of serotonin syndrome can occur within minutes to hours of taking a medication or combination of drugs that increase serotonin levels in the body. If you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms after taking drug or using substances that affect serotonin levels, seek immediate medical attention. Serotonin syndrome can become life-threatening if left untreated.
Can marijuana cause serotonin syndrome?

Marijuana use alone is generally not considered a cause of serotonin syndrome, but it is important to note that marijuana can interact with other drugs that affect serotonin levels and potentially contribute to the development of serotonin syndrome.
Serotonin syndrome is a potentially life-threatening condition caused by an excessive amount of serotonin in the brain. It is most commonly associated with the use of certain medications that affect serotonin levels, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), and some opioid pain medications. Serotonin syndrome can also occur when these medications are taken in combination with each other or with other drugs that affect serotonin levels.
While marijuana itself is not known to cause serotonin syndrome, it can interact with other drugs that affect serotonin levels and increase the risk of developing the condition. For example, marijuana may enhance the effects of SSRIs, which can increase serotonin levels in the brain and potentially lead to serotonin syndrome. Additionally, marijuana may interact with other drugs that affect serotonin levels, such as MAOIs, and increase the risk of serotonin syndrome.
If you are taking medications that affect serotonin levels and are considering using marijuana, it is important to discuss this with your healthcare provider to determine if it is safe for you to do so.
Can CBD cause serotonin syndrome?
While CBD (cannabidiol) is generally considered safe and well-tolerated, there have been a few reports of it causing serotonin syndrome, particularly when used in combination with other drugs that affect serotonin levels.
CBD has been shown to affect serotonin levels in animal studies, but its effects on serotonin levels in humans are not well understood. Some studies have suggested that CBD may increase serotonin levels in the brain, while others have suggested that it has no effect on serotonin levels.
There have been a few case reports of CBD causing serotonin syndrome, particularly when used in combination with other drugs that affect serotonin levels. However, these reports are rare and more research is needed to fully understand the potential risks of CBD in relation to serotonin syndrome.
Summary
Serotonin syndrome is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when there is an excess of serotonin in the body. It can be caused by taking certain medications or drugs that increase serotonin levels, or by combining multiple medications or drugs that affect serotonin. Symptoms of serotonin syndrome can range from mild to severe and may include agitation, confusion, high blood pressure, rapid heart rate, muscle rigidity, and seizures.
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. While THC does not directly increase serotonin levels, it can affect the way serotonin is processed in the body. Some studies have suggested that THC may increase the release of serotonin in certain parts of the brain, while others have found that it may decrease serotonin levels in other areas.
Overall, the relationship between THC and serotonin is complex and not fully understood. While it is possible that THC could contribute to serotonin syndrome in certain circumstances, such as when combined with other drugs that affect serotonin, more research is needed to fully understand this potential interaction.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does weed affect dopamine?
Weed can affect dopamine levels in the brain in several ways. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that is involved in regulating movement, motivation, and reward, among other things. THC, the primary psychoactive component in marijuana, can affect dopamine levels in several ways.
Firstly, THC can increase dopamine release in certain parts of the brain, particularly in the mesolimbic pathway, which is involved in reward and motivation. This increase in dopamine release can lead to the feelings of pleasure and euphoria that are often associated with marijuana use.
Secondly, THC can also indirectly affect dopamine levels by inhibiting the activity of GABA, another neurotransmitter that normally acts to inhibit dopamine release. By inhibiting GABA, THC can indirectly increase dopamine release.
Finally, chronic marijuana use can lead to changes in the brain’s dopamine system, including changes in the number and sensitivity of dopamine receptors. This can lead to a reduction in dopamine release over time and may contribute to some of the negative effects of chronic marijuana use, such as reduced motivation and pleasure in activities that would normally be rewarding.
What drugs cause serotonin syndrome?
It can be caused by taking drugs that increase serotonin levels or by combining multiple drugs that affect serotonin levels. Some drugs that can cause serotonin syndrome include:
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) – These are a type of antidepressant medication that is commonly prescribed to treat depression and anxiety.
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) – These are another type of antidepressant medication that work by increasing the levels of serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain.
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) – These are a type of antidepressant medication that can increase serotonin levels and are typically only used when other treatments have not been effective.
- Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) – These are an older class of antidepressant medication that can also increase serotonin levels.
- Triptans – These are medications used to treat migraines and can also increase serotonin levels.
- Street drugs such as ecstasy (MDMA) and amphetamines can also cause serotonin syndrome.
It is important to note that this list is not exhaustive, and there may be other drugs or combinations of drugs that can cause serotonin syndrome.
Does weed cause depression?
The relationship between marijuana use and depression is complex and not fully understood. While some people use marijuana to help alleviate symptoms of depression, research suggests that heavy and chronic marijuana use may increase the risk of developing depression.
Studies have shown that marijuana use can have both short-term and long-term effects on mood. Short-term effects can include feelings of euphoria and relaxation, while long-term effects can include changes in brain structure and function, as well as an increased risk of developing mental health disorders such as depression.
In particular, heavy and chronic use of marijuana has been associated with an increased risk of developing depression, particularly in people who have a genetic vulnerability to the disorder. One study found that heavy marijuana users were more than twice as likely to develop depression compared to non-users.
It is important to note, however, that not everyone who uses marijuana will experience negative effects on their mood or mental health. Factors such as the amount and frequency of use, as well as individual differences in genetics and mental health history, can all play a role in determining the effects of marijuana use on mood.