Hash production has come a long way over the millennia, from hand-crushing to modern methods of commercial carbon dioxide extraction. While the ways it is used have remained largely unchanged, production methods have evolved considerably.
Hash, also known as hash, is an extract of cannabis trichomes containing the psychoactive compound THC and over a hundred other cannabinoids, including CBD and CBN. There are many methods of making it, many of which have been developed by traditional cannabis communities, such as those in the Rif Valley in Morocco, over the centuries.
Dry hash

One of the most common methods of making cannabis is dry sieving. In this process, fully grown, harvested and dried cannabis plants are sifted or shaken through a fine-mesh sieve to collect the crystalline resin as a powder which is separated from the plant. The quality of the hash depends on the mesh size of the sieve: the finer the mesh, the higher the quality of the hash, while the larger mesh sieve produces lower quality hash with more plant inclusions.
An important factor when using the dry sieving method is the length and intensity of the shaking which affects the final result. For high quality dry hash such as Double Zero, King Hassan and Ketama Gold, good quality plants are shaken on a fine sieve for a minute or two so that only the most mature and fully developed trichomes are picked. Prolonged shaking, in turn, results in lower quality hash with more plant material.
Hand rubbed hash

Just after the dry sifting method, hand rubbing is the second most popular method of hashish production. This approach is heavily used in countries such as India, Nepal, Afghanistan and Pakistan, as well as in lesser-known hashish producing countries including Bhutan and Myanmar. Hand-grind hash has become almost as common globally as dry sieve hash, thanks to exports.
In the hand-grinding process, cannabis resin is usually harvested from living plants that are still in the field. Hash producers literally run through fields of mature cannabis plants, collecting the sticky resin on their skin, which is then rolled into balls and left to harden. In the case of charas (Indian hashish obtained by hand-grinding) this «curing» process can take several years.
The quality of hand-crushed hashish can depend on the quality of the plant and the precautions you take to avoid contaminating the plant material. The time required to properly process hash is also important, not only for hand-ground hash but also for hash produced using any other processing method. But in the case of hashish produced by hand-grinding, the drying stage is particularly important as fresh plants contain a lot of moisture that has to be removed.
«Pure» Cannabis Extracts

Modern methods of extracting resin from cannabis are becoming increasingly sophisticated, resulting in products of the highest quality and effectiveness. With the approval of the medical cannabis industry in the United States and other countries, medical cannabis produced by some licensed and regulated producers is probably one of the best cannabis products available today.
Usually solvents such as alcohol or butane, or simply ice water, are used to make high quality extracts. Theoretically, to create hashish in any technique, crystals must be separated. However, dry sieving or hand rubbing methods will never achieve the level of purity that can be achieved with more precise forms of mechanical or chemical extraction.
In extraction using water or solvent, the crystals are separated from the rest of the plant material and suspended in solution, then filtered through a fine sieve and dried. They are then left to harden for several weeks to make sure that all traces of water or solvent have completely evaporated.
Extraction with water or bubble hash
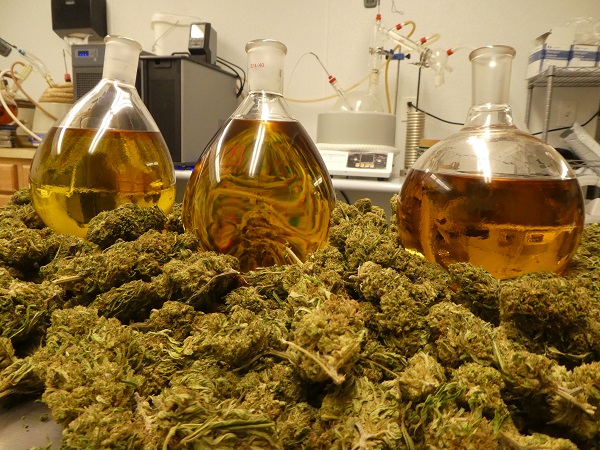

The water extraction process, also known as «bubble hash» creation, uses different sized mesh bags that are placed one inside the other in a bucket or similar container. The bag with the largest mesh size (usually 220 microns or larger) is filled with fresh or dried cannabis.
This bag is then placed in a bucket or a special washing machine (such as the famous Pollinator, Ice-o-lator models and so on) filled with cold water. The water is stirred vigorously, causing the crystals to freeze and separate, which then float up in solution. This mixture is then poured into a bucket lined with bags and passed through meshes of varying sizes, trapping larger particles and residual plant material.
This approach produces several types of hash of varying quality. Usually the best quality is the hash produced by using the smallest mesh size (25-45 microns). Mesh sizes with larger mesh sizes (90-220 microns) produce lower quality hash containing more plant material.
Solvent extraction

This approach uses alcohol or butane gas to extract the crystals from the residual plant material. Despite the need to use a grid, one size is usually chosen, which ensures consistent hash quality, unlike the variety of variants obtained by water extraction.
Since THC and other cannabinoids dissolve in alcohol and other solvents, the resin dissolves in them and can then be separated. With butane, HoneyBee-type devices are useful for small batch production; for larger quantities, specialized equipment is recommended.
The HoneyBee is a plastic cylinder with a small hole for a gas cylinder at one end and a series of small holes at the other. When compressed gas is fed into the plastic cylinder, it expands and pushes the dissolved resin through the holes into the prepared container.
As for alcohol, the isopropyl quick flush method is becoming increasingly popular and is actively used by medical drug manufacturers in the United States. In this case, cannabis is mixed with pure isopropyl alcohol for a very short time: no more than thirty seconds is recommended to ensure a high quality product. The mixture is then passed through a sieve and left to dry.
As technology advances, the cannabis industry is developing more stable and safer solvents for use in solvent extraction. One such example is the CO2 extraction method. In this method, frozen carbon dioxide is pumped through plant material to extract cannabinoids and other compounds. This extraction method has become the preferred method for many producers because the final product contains no residual solvent.
Rosin
Rosin is a relatively new innovation in hash production. This method is based on using heat to melt the resin on the absorbent material. When the resin solidifies again, it is extracted from the material and spread over its surface.
An example of this approach would be using a hair straightener and a sheet of parchment paper. A dry hemp bud is placed between a folded sheet of parchment paper. Then the paper with the bud is pressed with the iron until the resin begins to melt and soak into the paper. The bud is then removed (remember to unplug the iron), and after a few minutes, something resembling shards or wax is formed on the parchment paper, which can be collected.
This method is a great example of obtaining cannabis extract without using a solvent. It is safe, easy to prepare at home, and highly effective. Even in the United States, commercial producers have begun to use this approach to obtain rosin on a commercial scale.
What is the best type of hash?

Solvent-derived hashish is probably the purest and most concentrated form available today. Thanks to improvements in technology, the problem of solvent residue has been largely solved. However, working with flammable volatile compounds can be risky. Therefore, creating your own extracts using solvent should only be done by those who are aware and experienced in dealing with such risks.
The process of making aqueous hash is also complex, but has virtually none of the risks inherent in solvent extraction. The results can be comparable to pure solvent extracts, but the lower quality varieties can be disappointing. Many cannabis enthusiasts prefer aqueous extracts over solvent extracts because they are considered «cleaner» due to the lack of contact with potentially harmful solvents.
However, for those who value flavor more than strength, dry sieving or hand rubbing are often preferred over extracts. Although extracts are pure and strong, they are often inferior in flavor because the terpenes in the plant material can be washed out. Because more plant material remains in dry sieving and hand-grinding, the flavor of the original plant is often retained.