Inflammation is a natural response of the immune system to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can lead to a range of health problems. There is growing interest in the use of cannabis-based treatments for inflammation, and in particular, the potential of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, to reduce inflammation. While research on the subject is still limited, preliminary studies suggest that THC may have anti-inflammatory properties that could make it a useful treatment for conditions such as arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and Crohn’s disease. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the science behind THC and inflammation, and explore the potential benefits and risks of using THC as an anti-inflammatory agent.
How does cannabis fight inflammation?

Cannabis has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, and research suggests that tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, plays a key role in reducing inflammation. There are several mechanisms by which cannabis and THC may fight inflammation in the body.
One of the primary ways that cannabis and THC reduce inflammation is by interacting with the endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS is a complex signaling system that helps regulate many physiological processes, including inflammation. The ECS consists of three main components: cannabinoid receptors, endocannabinoids (cannabinoids produced naturally by the body), and enzymes that break down endocannabinoids. THC and other cannabinoids in cannabis can bind to cannabinoid receptors in the ECS, which may modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation.
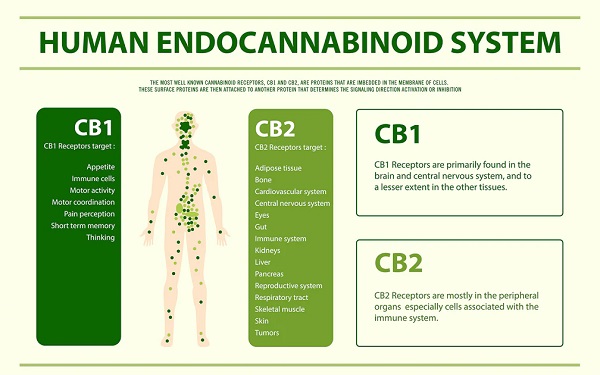
THC has been shown to bind primarily to the CB1 receptor in the ECS, which is found mainly in the central nervous system. However, it can also bind to the CB2 receptor, which is found primarily in the immune system and peripheral tissues. Activation of the CB2 receptor by THC has been shown to reduce inflammation in various models of disease, including autoimmune disorders, neuroinflammation, and gastrointestinal inflammation.
In addition to interacting with the ECS, THC may also reduce inflammation by suppressing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Cytokines are signaling molecules that are produced by immune cells and play a key role in inflammation. Some cytokines, such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), are known to contribute to the development of chronic inflammation. THC has been shown to reduce the production of these cytokines in preclinical studies, which suggests that it may have anti-inflammatory effects.
Another mechanism by which THC may reduce inflammation is by acting as an antioxidant. Oxidative stress, which is caused by an imbalance between antioxidants and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the body, is known to contribute to inflammation. THC and other cannabinoids in cannabis have been shown to have antioxidant properties that can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation.
Overall, the anti-inflammatory effects of cannabis and THC are likely due to a combination of these mechanisms, as well as others that are still being studied. While there is evidence to suggest that cannabis and THC may have anti-inflammatory properties, more research is needed to fully understand how they interact with the body and how they can be used safely and effectively for anti-inflammatory purposes.
Should you try CBD for inflammation?
The decision to try CBD (cannabidiol) for inflammation is ultimately up to the individual and should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional. While CBD has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, it is important to understand that it is not a cure for inflammatory conditions and should not be used as a substitute for conventional medical treatment.
That being said, there is growing interest in the potential of CBD as a natural alternative to conventional anti-inflammatory drugs. Unlike THC, CBD does not produce a psychoactive effect and is generally well-tolerated by most people. CBD has been shown to reduce inflammation by interacting with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which helps regulate many physiological processes, including inflammation.
CBD has been studied for its potential to reduce inflammation in a variety of conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and inflammatory bowel disease. While the results of these studies are promising, more research is needed to fully understand the effects of CBD on inflammation and how it can be used safely and effectively.
It is important to note that CBD is not regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and there is currently no standard dosing protocol for CBD. If you are considering trying CBD for inflammation, it is important to choose a reputable brand and start with a low dose, gradually increasing as needed. You should also talk to your healthcare provider to ensure that CBD is safe and appropriate for your individual needs and medical history, and to discuss potential interactions with other medications you may be taking.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CBD for Inflammation
CBD (cannabidiol) has been studied for its potential to reduce inflammation in a variety of conditions, and while there are potential advantages to using CBD for inflammation, there are also some potential disadvantages to consider.
Advantages:
- Anti-inflammatory properties: CBD has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which makes it a potentially useful treatment for a range of inflammatory conditions, including arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and multiple sclerosis.
- Non-psychoactive: Unlike THC, CBD is non-psychoactive and does not produce the “high” associated with cannabis use. This makes it a more accessible option for those who want to use cannabis for its potential therapeutic benefits without experiencing the psychoactive effects of THC.
- Generally well-tolerated: CBD is generally well-tolerated by most people and has few known side effects. While some people may experience mild side effects like drowsiness or dry mouth, these are typically not serious and can be managed with adjustments to dosing.
- Natural alternative to conventional drugs: CBD may be a natural alternative to conventional anti-inflammatory drugs, which can have serious side effects and may not be suitable for everyone. CBD may be a useful option for those who prefer a natural approach to managing their inflammation.
Disadvantages:
- Lack of regulation: CBD is not regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which means that there is no standard dosing protocol or quality control standards for CBD products. This can make it difficult to determine the quality and safety of CBD products, and may increase the risk of contamination or adulteration.
- Limited research: While there is growing interest in the potential of CBD for inflammation, there is still a limited amount of research on the topic. More research is needed to fully understand the effects of CBD on inflammation, as well as the long-term safety and efficacy of CBD as a treatment for inflammatory conditions.
- Potential drug interactions: CBD may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners and seizure medications. It is important to talk to your healthcare provider before using CBD if you are taking any medications, to ensure that it is safe and appropriate for you.
- Variable effectiveness: CBD may be effective for some people and not for others, and the effectiveness of CBD for inflammation may vary depending on the type and severity of the inflammation. It is important to have realistic expectations and to be willing to try different dosages or formulations of CBD to find what works best for you.
CBD may be a useful option for managing inflammation in certain individuals, but it is important to consider the potential advantages and disadvantages before using CBD for this purpose. It is recommended to speak with a healthcare professional before using CBD, and to choose high-quality, reputable products from trusted sources.
What causes chronic inflammation?
Chronic inflammation is a prolonged and persistent immune response that can damage tissues and organs. There are many factors that can contribute to chronic inflammation, including:
- Autoimmune disorders: Autoimmune disorders occur when the immune system attacks healthy tissues and organs, causing chronic inflammation. Examples of autoimmune disorders include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis.
- Infections: Chronic infections, such as hepatitis B or C, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and tuberculosis, can lead to chronic inflammation.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to environmental pollutants, such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, and pesticides, can trigger chronic inflammation.
- Stress: Chronic stress can cause inflammation by increasing the production of stress hormones like cortisol, which can suppress the immune system and contribute to chronic inflammation.
- Poor diet: A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats can lead to chronic inflammation. On the other hand, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can help reduce inflammation.
- Obesity: Obesity is associated with chronic inflammation, and excess fat tissue can produce inflammatory chemicals.
- Genetic factors: Certain genetic mutations can increase the risk of chronic inflammation.
Chronic inflammation can contribute to the development of many diseases, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. Therefore, it is important to address the underlying causes of chronic inflammation and take steps to reduce inflammation through healthy lifestyle habits, stress management, and medical treatment when necessary.
Inflammation and medical cannabis: what are medical cannabis patients saying?

Medical cannabis is becoming an increasingly popular alternative for patients suffering from chronic inflammation.
Patients who use medical cannabis to manage inflammation report that it helps to reduce pain, swelling, and stiffness in joints and muscles. Cannabis is also reported to improve mobility and overall quality of life. Many patients report that cannabis is more effective than traditional anti-inflammatory medications and has fewer side effects.
One of the reasons why cannabis is effective in managing inflammation is due to its interactions with the endocannabinoid system (ECS).
Medical cannabis patients have reported that different strains of cannabis can have varying effects on inflammation. For example, some strains with higher levels of THC may be more effective in reducing inflammation, while others with higher levels of CBD may be more effective in managing pain associated with inflammation.
Additionally, medical cannabis patients have reported that the delivery method of cannabis can also affect its effectiveness in managing inflammation. Smoking or vaporizing cannabis may provide more immediate relief, while edibles or topicals may provide longer-lasting relief.
It is important to note that while many medical cannabis patients report positive results in using cannabis to manage inflammation, more research is needed to fully understand the effectiveness of cannabis in treating inflammation and to develop evidence-based treatment guidelines. Patients considering using cannabis for inflammation should consult with a healthcare professional to determine if it is a suitable treatment option for their specific condition.
Conclusion
THC has shown promising potential in managing inflammation. Research has suggested that THC may be effective in reducing inflammation associated with a variety of medical conditions. The anti-inflammatory properties of THC are believed to be due to its interactions with the endocannabinoid system and other physiological pathways.
While THC has shown potential in managing inflammation, it is important to note that it may not be suitable for everyone. THC can produce psychoactive effects and may cause side effects. Additionally, its use may be restricted or illegal in some jurisdictions.
More research is needed to fully understand the effects of THC on inflammation and to develop evidence-based treatment guidelines. Patients considering using THC for inflammation should consult with a healthcare professional to determine if it is a suitable treatment option for their specific condition.
Overall, while THC shows promise in managing inflammation, it is important to weigh its potential benefits against potential risks and side effects. Patients should consider a range of treatment options and work with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that best suits their needs.
Frequently asked questions
What type of CBD is good for inflammation?
There are different types of CBD products available, and some may be more effective in managing inflammation than others. When considering CBD products for inflammation, it is important to understand the different types of CBD available, including full-spectrum CBD, broad-spectrum CBD, and CBD isolate.
- Full-spectrum CBD contains all the compounds found in the cannabis plant, including THC, other cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids. Research suggests that full-spectrum CBD may be more effective in managing inflammation due to the entourage effect, which is the theory that the combination of all cannabis compounds works together to provide greater therapeutic benefits.
- Broad-spectrum CBD contains all the compounds found in full-spectrum CBD except for THC. This type of CBD may be a good option for individuals who want to avoid THC but still benefit from the entourage effect.
- CBD isolate is pure CBD that has been extracted from the cannabis plant and contains no other compounds. While CBD isolate may be effective in managing inflammation, some research suggests that it may not be as effective as full-spectrum CBD due to the lack of other cannabis compounds.
Ultimately, the best type of CBD for inflammation may depend on individual preferences and needs. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine which type of CBD is the most suitable option for managing inflammation associated with a specific medical condition.
Does THC help with inflammation?
Research suggests that THC may help with inflammation. THC has been found to have anti-inflammatory properties that may be effective in reducing inflammation associated with a variety of medical conditions, including autoimmune disorders, arthritis, and Crohn’s disease.
Studies have suggested that THC works by interacting with the endocannabinoid system and other physiological pathways to reduce inflammation. THC has been found to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and promote the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, which helps to reduce inflammation.
However, it is important to note that THC can produce psychoactive effects and may cause side effects, such as dizziness, fatigue, and impaired cognitive function. Additionally, its use may be restricted or illegal in some jurisdictions.
More research is needed to fully understand the effects of THC on inflammation and to develop evidence-based treatment guidelines.
Are THC gummies good for inflammation?
THC gummies may have potential in managing inflammation due to the anti-inflammatory properties of THC. However, it is important to note that THC gummies may not be the best option for everyone and should be used with caution.
When consuming THC gummies, the effects of THC are generally delayed and longer-lasting compared to other forms of cannabis consumption, such as smoking or vaping. This can be beneficial for individuals who require longer-lasting pain relief. However, it also means that it can be more difficult to control the dosage, which increases the risk of side effects and other adverse reactions.
How much THC do I need to relieve inflammation?
The amount of THC needed to relieve inflammation can vary depending on several factors, including the severity of inflammation, the individual’s body chemistry, and their tolerance to THC.
There is no established dosage for THC in managing inflammation, as research in this area is still limited. However, some studies have suggested that doses of THC ranging from 2.5mg to 20mg per day may be effective in reducing inflammation associated with certain medical conditions, such as Crohn’s disease and multiple sclerosis.
It is important to note that higher doses of THC may produce more potent anti-inflammatory effects, but they also increase the risk of adverse effects and may not be suitable for everyone. Additionally, the optimal dosage may vary depending on the individual’s specific medical condition and overall health.
It is recommended to start with a low dose of THC and gradually increase as needed, under the guidance of a healthcare professional. This allows individuals to determine their optimal dosage while minimizing the risk of side effects and adverse reactions.
Overall, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage of THC for managing inflammation associated with a specific medical condition, and to source high-quality products from reputable manufacturers.