Marijuana, also known as cannabis, is a plant that has been used for both medicinal and recreational purposes for thousands of years. One of the main active ingredients in marijuana is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which has been found to have a range of potential health benefits. However, recent research has also suggested that THC may have an unexpected role in fighting bacterial infections. In particular, there is growing interest in the potential of THC as an antibiotic, or as a complementary therapy to conventional antibiotics. This article will explore the current state of research on the use of THC as an antibiotic, as well as its potential benefits and limitations.
What are antibiotics and how do they affect your body?
Antibiotics are a type of medication used to treat bacterial infections. They work by either killing the bacteria or preventing them from multiplying, thereby allowing the body’s immune system to eliminate the infection.
There are many different types of antibiotics, each with its own mechanism of action and spectrum of activity against different types of bacteria. Some antibiotics are broad-spectrum, meaning they are effective against a wide range of bacteria, while others are narrow-spectrum and are only effective against specific types of bacteria.
When you take an antibiotic, it travels through your bloodstream and reaches the site of the infection. Once there, it either kills the bacteria directly or inhibits their growth and replication. However, antibiotics can also affect the healthy bacteria that live in your body, known as microbiome. This can sometimes result in unwanted side effects, such as diarrhea, upset stomach, and yeast infections.
In addition to their effects on the microbiome, antibiotics can also interact with other medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness or causing unwanted side effects.
It is also worth noting that antibiotics only work against bacterial infections, not viral infections such as the common cold or the flu. Taking antibiotics unnecessarily or inappropriately can contribute to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which pose a significant threat to public health.
Overall, antibiotics are an important tool in the treatment of bacterial infections, but they must be used responsibly and only when necessary to ensure their continued effectiveness and safety.
The dangers of antibiotic-resistant bacteria
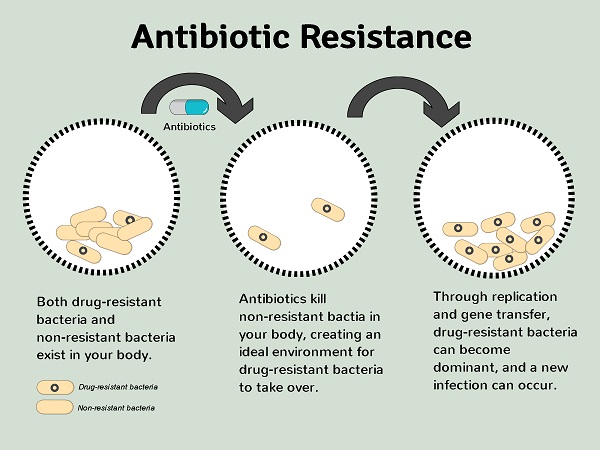
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are a growing threat to global public health. These bacteria have developed the ability to resist the effects of antibiotics, making it much more difficult to treat infections and putting patients at greater risk of serious illness, disability, and death. In recent years, antibiotic-resistant bacteria have become increasingly common, and the problem is exacerbated by the overuse and misuse of antibiotics, as well as poor infection control practices.
The dangers of antibiotic-resistant bacteria are many. For example, patients infected with these bacteria may experience longer hospital stays, more severe infections, and increased risk of complications such as sepsis. In some cases, infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria may be untreatable, leading to increased morbidity and mortality.
In addition to the direct health risks posed by antibiotic-resistant bacteria, there are also significant economic costs associated with these infections. These costs include the direct costs of treating infections, as well as the indirect costs of lost productivity and increased healthcare spending.
Can marijuana replace antibiotics?

While there is some research suggesting that certain compounds in marijuana, such as cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), may have antibacterial properties, there is currently no evidence to suggest that marijuana can replace antibiotics in the treatment of bacterial infections.
Antibiotics work by specifically targeting and killing bacterial cells, while marijuana compounds may have more general antibacterial properties that could potentially be useful in the development of new treatments. However, research in this area is still in its early stages, and much more research is needed to fully understand the potential antibacterial effects of marijuana compounds and how they could be used in clinical practice.
In addition, it is important to note that the use of marijuana for medicinal purposes is still largely unregulated and not widely accepted in the medical community. While some states in the US have legalized marijuana for medicinal use, there is still limited research on its safety and effectiveness, and there are significant legal and ethical concerns surrounding its use as a treatment for bacterial infections.
Furthermore, it is important to recognize that antibiotic resistance is a serious global health threat, and simply replacing antibiotics with another treatment, such as marijuana, may not be a sustainable solution.
Will cannabis reduce the effectiveness of my antibiotics?
There is limited research on the potential interactions between cannabis and antibiotics, so it is difficult to provide a definitive answer. However, there is some evidence to suggest that cannabis may interfere with the effectiveness of certain antibiotics.
One study found that THC, one of the primary active compounds in cannabis, may decrease the effectiveness of certain antibiotics, including erythromycin and tetracycline. The study found that THC reduced the ability of these antibiotics to kill bacteria in laboratory tests, suggesting that it may interfere with their mechanism of action.
In addition, cannabis use can also affect the way that the liver metabolizes certain medications, including antibiotics. This can potentially lead to higher or lower than expected levels of the medication in the body, which can affect its effectiveness and increase the risk of side effects.
It is therefore important to inform your healthcare provider if you are using cannabis while taking antibiotics. They can help determine whether there is a potential for interaction and adjust your medication as necessary to ensure its effectiveness and safety.
Is it safe to use cannabis while taking antibiotics?
It is generally not recommended to use cannabis while taking antibiotics, as there is limited research on the potential interactions between the two and the effects on the body.
Antibiotics are powerful medications used to treat bacterial infections, and it is important to take them as prescribed by your healthcare provider to ensure their effectiveness and avoid the development of antibiotic resistance.
What are the risks of using cannabis while taking antibiotics?
The risks of using cannabis while taking antibiotics are not fully understood due to limited research on the potential interactions between the two. However, there are some potential risks to consider.
- Firstly, cannabis use can potentially interfere with the effectiveness of antibiotics. For example, one study found that THC, one of the primary active compounds in cannabis, may reduce the effectiveness of certain antibiotics, such as erythromycin and tetracycline, by reducing their ability to kill bacteria in laboratory tests.
- Secondly, cannabis use can affect the way that the liver metabolizes certain medications, including antibiotics. This can potentially lead to higher or lower than expected levels of the medication in the body, which can affect its effectiveness and increase the risk of side effects.
In addition, cannabis use can cause side effects such as dizziness, confusion, and changes in heart rate and blood pressure. These effects may be more pronounced when used in combination with antibiotics, which can also have their own set of side effects.
Moreover, it is also important to note that using cannabis while taking antibiotics can potentially lead to drug interactions with other medications you may be taking, which can be harmful to your health.
It is therefore important to consult with your healthcare provider before using cannabis while taking antibiotics to ensure its safety and effectiveness.
When not to use antibiotics with marijuana?

It is generally not recommended to use marijuana while taking antibiotics, as marijuana use can potentially interfere with the effectiveness of antibiotics and affect the way that the liver metabolizes certain medications, which can lead to higher or lower levels of the medication in the body.
Moreover, there are some specific circumstances in which you should avoid using antibiotics with marijuana, including:
- If you have a history of drug interactions: If you have experienced drug interactions in the past, it is important to be cautious when using antibiotics with marijuana and to consult with your healthcare provider before using them together.
- If you have a history of liver disease: Marijuana use can affect the way that the liver metabolizes certain medications, including antibiotics, and may exacerbate liver disease symptoms.
- If you are pregnant or breastfeeding: The use of marijuana during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not recommended due to potential risks to the developing fetus or newborn.
- If you have a history of mental health conditions: Marijuana use can exacerbate symptoms of mental health conditions, and may interact with certain medications used to treat these conditions.
- If you are taking medications that may interact with marijuana: Certain medications, such as benzodiazepines and opioids, may interact with marijuana and lead to harmful effects.
Overall, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider before using antibiotics with marijuana, and to inform them of any other medications you are taking or any health conditions you have. They can help determine whether there is a potential for interaction and adjust your medication as necessary to ensure its effectiveness and safety.
Alternatives while taking antibiotics

While it is generally recommended to avoid using marijuana while taking antibiotics, there may be some alternative types of marijuana that have fewer interactions with antibiotics. However, it is important to note that there is limited research on this topic, and individual reactions to different strains of marijuana can vary widely.
If you are considering using marijuana while taking antibiotics, here are some alternative types of marijuana that may have fewer interactions:
- CBD-dominant strains: CBD (cannabidiol) is a non-psychoactive compound found in marijuana that has been shown to have potential health benefits, including reducing inflammation and anxiety. CBD-dominant strains have higher levels of CBD and lower levels of THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the psychoactive compound in marijuana. This may reduce the risk of interactions with antibiotics and minimize the risk of side effects.
- Indica strains: Indica strains of marijuana are generally considered to have more calming and relaxing effects than sativa strains. This may be beneficial if you are experiencing anxiety or insomnia related to an infection, but it is important to note that individual reactions to different strains of marijuana can vary widely.
- Edibles or topicals: Edibles or topicals, which are applied to the skin, may have fewer interactions with antibiotics compared to smoking or vaporizing marijuana. However, it is important to note that edibles can take longer to take effect and may have a longer duration of action compared to smoking or vaporizing.
It is important to talk to your healthcare provider before using any form of marijuana while taking antibiotics. They can help you determine whether there is a potential for interaction and advise you on the best course of treatment for your specific condition.
How does cannabis interact with drugs?
Cannabis can interact with drugs in several ways, including:
- Metabolism: Cannabis can affect the metabolism of other drugs in the body, which can lead to either decreased or increased effectiveness of the drugs. This is because cannabis can interact with the enzymes responsible for metabolizing drugs in the liver.
- Blood pressure: Cannabis can cause a temporary increase in heart rate and blood pressure. If you are taking medications that affect your blood pressure, such as beta blockers or calcium channel blockers, cannabis use may interfere with their effectiveness.
- Sedation: Cannabis can cause sedation and drowsiness, which can be dangerous if you are taking medications that also cause drowsiness, such as opioids, benzodiazepines, or antihistamines.
- Psychiatric medications: Cannabis can interact with psychiatric medications, such as antidepressants or antipsychotics, which can affect their effectiveness and potentially cause adverse effects.
- Blood thinners: Cannabis can interact with blood thinners, such as warfarin, which can increase the risk of bleeding.
It is important to talk to your healthcare provider about any drugs you are taking, including cannabis, as well as any medical conditions you have.
Conclusion
While there is some evidence to suggest that THC, the psychoactive component of marijuana, may have antibacterial properties, it is not a replacement for antibiotics. Antibiotics are still the most effective treatment for bacterial infections, and it is important to use them as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Furthermore, there are potential interactions between marijuana and antibiotics, which can reduce the effectiveness of the antibiotics and lead to adverse effects. Therefore, it is generally recommended to avoid using marijuana while taking antibiotics.
If you are considering using marijuana for medicinal purposes, it is important to talk to your healthcare provider about potential interactions with any medications you are currently taking, including antibiotics. They can help you determine the best course of treatment for your specific condition.
Overall, while there is ongoing research on the potential benefits and risks of using marijuana in conjunction with antibiotics, it is important to prioritize safe and effective treatment for bacterial infections.