In recent years, the legal landscape surrounding the use of cannabis and its psychoactive component, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), has undergone significant transformations across the United States. While some states have embraced comprehensive legalization for both medical and recreational purposes, others have maintained strict prohibition. Georgia, situated in the southeastern region of the country, has found itself amidst this evolving legal discourse on THC.
Georgia’s stance on THC has generated considerable attention and debate, as it navigates a delicate balance between public health concerns, patient access to medicinal cannabis, and changing societal attitudes towards cannabis use. This article delves into the complex and often confusing legal status of THC in the state of Georgia.
Is marijuana legal in Georgia?
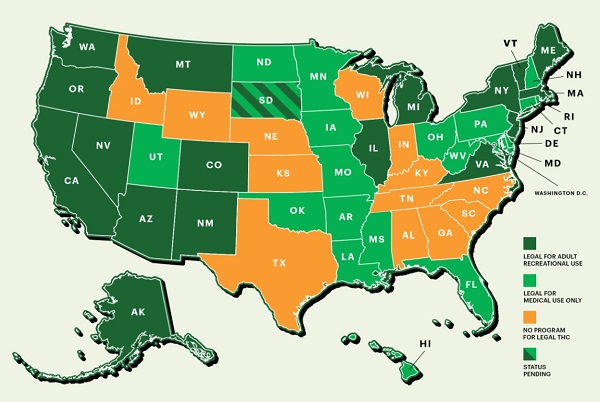
No, marijuana remains illegal in Georgia. Although Atlanta decriminalized the possession of marijuana in 2017, it’s important to clarify that this action did not legalize marijuana. Mayor Kasim Reed signed the ordinance with a specific focus: to address the inequity in punishment for marijuana possession. A press release accompanying the ordinance emphasized that it doesn’t legalize or decriminalize marijuana possession. The rationale behind this move was rooted in research indicating that both White and Black Americans use marijuana at comparable rates, yet Black Americans face higher arrest and charge rates for possession.
Is recreational marijuana legal anywhere in Georgia?
No, recreational marijuana is still illegal throughout the state of Georgia. However, there is a provision that allows for the use of marijuana for medicinal purposes. Specifically, “qualified persons” are legally permitted to possess “up to 20 fluid ounces of low THC oil” in Georgia.
The legality of THC-O, Delta-8 THC, and Delta-9 THC in Georgia

- Delta-9 THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol): Delta-9 THC is the primary psychoactive compound found in cannabis and is generally illegal for recreational use in Georgia. Medical marijuana was legalized in Georgia for a limited set of medical conditions, but it was primarily focused on low-THC cannabis oil, not products containing high levels of Delta-9 THC.
- Delta-8 THC: Delta-8 THC is a compound found in small amounts in the cannabis plant. Its legal status can vary from state to state. In Georgia Delta-8 THC was not specifically addressed by state law. Some businesses were selling Delta-8 THC products, while others were cautious due to the unclear legal status.
- THC-O (Tetrahydrocannabinol-O-acetate): THC-O is a synthetic cannabinoid and is not naturally occurring in the cannabis plant. THC-O was not explicitly mentioned in Georgia’s state laws. Its legality would likely depend on how the state regulates synthetic cannabinoids.
It’s essential to verify the current laws and regulations in Georgia regarding THC-O, Delta-8 THC, and Delta-9 THC to ensure compliance with the most recent legal requirements.
Can I obtain a prescription for low-THC cannabis oil in Georgia, and if so, how does the process work?
It’s possible! To legally possess low-THC cannabis oil in Georgia, you need to be on the statewide registry. The process involves filling out two essential forms. First, there’s a waiver that both you and a physician must sign. Second, there’s a physician certification form, which your doctor will complete. Once the physician submits this form and it receives approval from the state, you’ll receive notification that you can obtain a Low-THC Oil Registry Card for a fee of $25. These cards are available at nearby public health offices.
How much THC is legal in Georgia?
Georgia had specific regulations regarding the allowable THC content in products for medical marijuana patients. In Georgia’s medical marijuana program, patients were allowed to possess and use low-THC cannabis oil with a maximum THC content of 5% by weight.
Please note that the legal landscape surrounding cannabis and THC content can change over time. Сonsulting with a legal expert or the Georgia Department of Public Health is the best course of action to obtain the most current and accurate information on THC limits in Georgia.
Which medical conditions are eligible for medicinal cannabis use in Georgia?
In Georgia, the following medical conditions are eligible for medicinal cannabis use:
- Epilepsy and seizure disorders.
- Certain types of cancer.
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
- Crohn’s disease.
- Parkinson’s disease.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Mitochondrial disease.
- Sickle cell disease.
- Tourette’s syndrome.
- Autism spectrum disorder.
- Epidermolysis bullosa.
- Alzheimer’s disease.
- AIDS.
- Peripheral neuropathy.
- Hospice patients.
- Intractable pain.
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Please note that the eligibility criteria and the list of qualifying conditions may evolve over time, so it’s essential to stay updated with the latest regulations and consult with a qualified healthcare professional for the most current information.
Is it possible to purchase medical marijuana in Georgia?
Unfortunately, no. According to state regulations, “The new law does not provide guidance on the production, sale, or transportation of low THC oil. Its sole purpose is to establish a process to protect qualified individuals from legal consequences for possessing low THC oil. The Georgia Department of Public Health does not have the authority to prescribe or distribute low THC oil.”
Are we likely to see recreational marijuana become legal in Georgia in the near future, or is it an uncertain prospect?
In contrast to numerous states nationwide embracing recreational cannabis, Georgia’s path to legalization appears to be an uphill battle. Atlanta’s “decriminalization” might be seen as a modest stride toward societal acceptance, potentially lending momentum to the broader statewide effort needed to achieve full legalization. However, the timeline and success of such an endeavor remain uncertain.
Summary
Georgia’s stance on THC legality has evolved over the years, primarily concerning the medical use of cannabis products. The state permitted registered medical marijuana patients to use low-THC cannabis oil with a maximum THC content of 5%. However, the legal frameworks surrounding cannabis and THC can change. Therefore, individuals and businesses should stay vigilant and regularly consult with legal experts and state authorities to ensure they are compliant with the most current and accurate regulations in Georgia.