Cannabinoids have been gaining popularity in recent years for their potential therapeutic benefits, and new cannabinoids are constantly being discovered and studied. Two such cannabinoids are HHC (hexahydrocannabinol) and THC-P (tetrahydrocannabiphorol), which are less well-known than more commonly recognized cannabinoids like THC and CBD. In this article, we will compare and contrast HHC and THC-P, examining their effects, potential benefits, and legality, as well as their chemical structure and how they are made.
HHC (Hexahydrocannabinol)
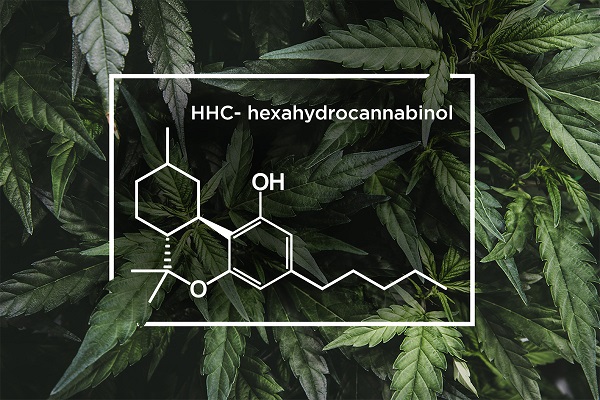
HHC, or hexahydrocannabinol, is a lesser-known cannabinoid that has gained attention in recent years due to its potential therapeutic benefits. It is produced through the conversion of other cannabinoids, such as cannabidiol (CBD), into their corresponding hexahydrocannabinols through a chemical process.
Like delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, HHC is known to have psychoactive effects. However, these effects are reported to be milder and more subtle than those of THC. Additionally, HHC is believed to have a number of potential therapeutic benefits.
One area of research in which HHC has shown promise is in the treatment of pain and inflammation. Studies in animal models have found that HHC is effective in reducing pain and inflammation, and may have potential for the treatment of conditions such as arthritis, neuropathic pain, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Another potential application of HHC is as an anti-cancer agent. Some research has suggested that HHC may have anti-tumor properties, and may be effective in inhibiting the growth of certain types of cancer cells. However, more research is needed to fully understand the potential of HHC as a cancer treatment.
HHC may also have potential as an anti-anxiety agent. Some research has suggested that HHC may have anxiolytic effects, and may be effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression. Additionally, HHC has been shown to have antioxidant properties, which may be beneficial for overall health and well-being.
While HHC is still a relatively new and understudied cannabinoid, its potential therapeutic benefits are beginning to be recognized. However, as with any cannabinoid or other natural product, it is important to approach HHC with caution and to consult with a healthcare provider before using it as a treatment for any medical condition.
What the high is like
As a relatively new and understudied cannabinoid, there is limited research available on what the high from HHC, or hexahydrocannabinol, is like. However, anecdotal reports suggest that the psychoactive effects of HHC are milder and more subtle than those of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis.
Some users report that the high from HHC is more functional and less impairing than that of THC, and that it may be more suitable for daytime use or for individuals who are sensitive to the psychoactive effects of THC. Others have described the high from HHC as calming, relaxing, and euphoric, with a clear-headedness and a lack of paranoia or anxiety.
It is important to note, however, that the effects of any cannabinoid can vary widely depending on factors such as dosage, individual biology, and the method of consumption. Additionally, as with any psychoactive substance, the effects of HHC may be unpredictable or undesirable for some individuals. Therefore, it is important to approach HHC and any other cannabinoid with caution and to use them responsibly.
Legality
The legality of HHC varies depending on the jurisdiction. In the United States, the legal status of HHC is complicated, but most experts agree it’s legal under current federal regulations (2018 Farm Bill) — as long as it’s derived from hemp and contains no more than 0.3% THC by dried weight. However, the legal status of HHC may be different at the state or local level, and laws regarding the production, sale, and use of HHC may vary.
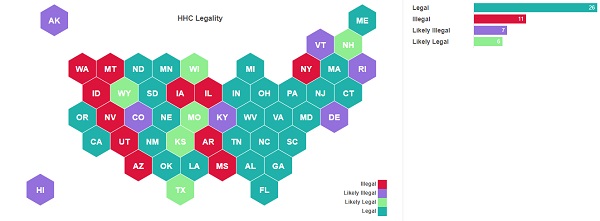
Therefore, individuals who choose to use HHC or other cannabinoids should be aware of the legal status in their jurisdiction and should take appropriate precautions to avoid legal issues.
THC-P (Tetrahydrocannabiphorol)

THC-P, or tetrahydrocannabiphorol, is a relatively new and understudied cannabinoid that is structurally similar to delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. While THC-P has not been extensively researched, initial studies suggest that it may be more potent and longer-lasting than THC.
While THC-P can be found in trace amounts in some cannabis strains, it is not typically found in high concentrations, and there are currently no known methods for extracting or synthesizing THC-P on a commercial scale.
Because THC-P is a relatively new and understudied compound, there is limited information available about its biosynthesis and metabolic pathways. Some researchers speculate that THC-P may be formed as a metabolic byproduct of other cannabinoids, or that it may be produced by specific strains of cannabis in response to environmental stressors.
What the high is like
One study found that THC-P was 30 times more potent than THC when administered to mice. Additionally, the effects of THC-P were longer-lasting than those of THC, with a duration of up to 48 hours. However, it is important to note that this study was not rigorously controlled, so the results should be interpreted with caution.
More recent research on THC-P is limited, but some anecdotal reports suggest that the effects of THC-P may be similar to those of THC, but with a faster onset and longer duration. Some users have reported feeling a more intense and longer-lasting high from THC-P, with effects that can last for several days.
It is important to note, however, that the effects of any cannabinoid can vary widely depending on factors such as dosage, individual biology, and the method of consumption. Additionally, as with any psychoactive substance, the effects of THC-P may be unpredictable or undesirable for some individuals. Therefore, it is important to approach THC-P and any other cannabinoid with caution and to use them responsibly.
Legality
The legal status of THC-P, or tetrahydrocannabiphorol, is not clear, as it is a relatively new and understudied cannabinoid. In the United States, for example, THC-P is fully federally legal and legal in most states:
- Alabama
- California
- Connecticut
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Missouri
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
However, the legal status of THC-P may be different at the state or local level, and laws regarding the production, sale, and use of THC-P may vary.
Therefore, individuals who choose to use THC-P or other cannabinoids should be aware of the legal status in their jurisdiction and should take appropriate precautions to avoid legal issues.
Additionally, as with any cannabinoid or other natural product, it is important to approach THC-P with caution and to consult with a healthcare provider before using it as a treatment for any medical condition.
Which cannabinoid will you choose?

The decision to use a particular cannabinoid is ultimately up to the individual, in consultation with their healthcare provider. Each cannabinoid has its own unique set of effects and potential benefits, and what may work well for one individual may not be as effective for another. The decision on which cannabinoid to use should take into account an individual’s health status, medical history, desired outcomes, and any potential risks or interactions with other medications.
Summary
HHC is similar to THC, but with a shorter duration and potentially less psychoactive effects. THC-P is a new cannabinoid that is still being studied, but early research suggests that it may be more potent and longer-lasting than THC.
Both cannabinoids are currently legal in some jurisdictions but may be illegal in others.
The decision on which cannabinoid to use should be made on an individual basis, taking into account an individual’s unique health needs and circumstances, and in consultation with a qualified healthcare provider.