THC-O doesn’t get much attention and isn’t suitable for DIY making like THC oil and CBD oil. In addition, to truly understand this unique substance, you will have to delve into some rather complex chemistry.
For this reason alone, THC-O is not suitable for most people. And it’s a shame, because with cannabis legalization sweeping the planet, THC-O is emerging from the shadows as a viable (and powerful) option for both recreational and medical use. In this article, we demystify THC-O to help you understand cutting-edge cannabis science and how it applies to your specific condition.
Fair warning! We’ll be dealing with a lot of chemical concepts (not to mention a lot of polysyllabic words), but we promise we’ll do our best to make it as accessible as possible!
What Is THC-O?
THC-O is shorthand (slang term) for THC-O-acetate, also called THC and ATHC acetate. That’s a lot of names for one substance. And yes, it can be confusing.
But what’s nice about cannabis culture is that it leans more towards brevity than precision (thank goodness, otherwise we’d always have to say or write “tetrahydrocannabinol”). So you’re likely to encounter THC-O or ATHC more often.
So, while we’re talking names, it’s important that you don’t confuse ATHC with THCA (or THCa). THCA is tetra-hydro-cannabinolic acid, the parent molecule of THC.
As the full name suggests, the “A” in THCA stands for acid. THCA is found naturally in raw cannabis and is converted to THC by decarboxylation. In ATHC, the “A” stands for acetate. This is the first significant difference.
The second important difference is that ATHC can only be produced under laboratory conditions. You can’t take a few tools on local equipment and whip up a batch of ATHC in your kitchen. The results will be catastrophic (that means fiery death, boys and girls).
So when it comes to ATHC and THCA, be sure to pay attention to where the “A” is in the name (and even uppercase or lowercase) because the two chemicals are completely different cases.
How Is It Made?

THC-O is made using high strength alcohol or acetone solvents where the molecules of the hemp plant are liquefied and extracted later. This extraction leaves behind a solvent with THC dissolved in it, creating a more potent and concentrated liquid than other hemp-derived products. It is three times stronger than Delta 9 THC and 5 times stronger than Delta 8 THC, which has the same basic structure but with added acetate.
This process is carried out in a laboratory according to the strict standards and criteria used by the cannabis industry to ensure the development of a high quality product.
What are the effects of THC-O?

As with other hemp-derived THC variations, the big question is, does THC-O give you a high? The answer is a firm yes. In fact, THC-O is said to be 2-3 times more potent than the delta-9 THC found in marijuana.
Measuring the effects of THC-O versus delta 8 THC, delta 10 THC or HHC is of course subjective. But according to most, THC-O takes you above delta 8 and gives you a much more intense experience than all other forms of THC.
Not only is THC-O stronger than other forms of THC, but the psychoactive effects are very different. Many consumers describe THC-O as having an almost psychedelic effect with borderline hallucinogenic effects. Both drug experts and vendors advise new users to try this powerful cannabinoid very slowly.
There is another reason to take your time: the effects of THC-O are always delayed. It’s a so-called “prodrug”, which means that the THC-O you swallow or inhale is not pre-heated like most THC is (a process called decarboxylation). Instead, the effects of THC-O are not felt until it has completely passed through the body – just like food products with THC.
So, whether you’re eating THC-O gummies or smoking a THC-O cart, you won’t feel any effect within 20-60 minutes. Because it’s so strong, it’s important to use a small amount first and then wait and see how you react before taking more.
Will THC-O show up in a drug test?
There is little to no research on how the body processes THC-O. But as far as the acetate ester form of THC, it seems almost certain that drug tests will detect THC metabolites in the blood, urine, or hair of a THC-O user.
The same warning applies to THC-O as to Delta-8, Delta-10, and GTS: If your employer tests for marijuana, it’s best to avoid THC-O.
Is THC-O safe?
THC-O is not safe to vape or smoke. THC-O is created by chemically converting CBD to either delta-9-THC or delta-8-THC and then converting those cannabinoids into their acetate ester form, which is called THC-O for short. Some studies show that, when heated sufficiently, THC-O’s thermal decomposition can produce a dangerous lung toxic substance called ketene.
The same process of thermal degradation causes vitamin E acetate to form ketene, the likely cause of the 2019 vaping lung injury that the CDC erroneously called “EVALI.” (Black market cannabis processors used vitamin E acetate to dilute THC oil to save money.)
The danger is not caused by marijuana itself or by vaping itself, but by the interaction of heat with the acetate form of various chemicals, including THC. In fact, any acetate ester can produce ketene when heated.
It is not known if the amount of ketene produced by a vape cart is enough to pose an immediate danger to the user, but it is possible. It is also possible that cumulative lung damage could be caused by repeated small exposures.
Based on this study, we urge cannabis users to avoid vaping or smoking THC-O or any acetate form of any cannabinoid. THC-O gummies and tinctures do not pose a health risk. The danger posed by heating THC-O is not present in edible forms. Since there are many non-inhaled options, THC-O fans should look for them.
The production of THC-O is definitely dangerous. Acetic anhydride is highly flammable and its use creates a fire and explosion hazard. As with butane hash oil (BHO), it can only be produced in properly equipped laboratories by people who are intimately familiar with the process. And even with experienced refiners, there remains the possibility that traces of the chemicals used to create THC-O could remain in the final product.
Is THC-O legal?
THC-O is no longer considered legal!
In the Farm Act of 2018, Congress legalized hemp and all its compounds and derivatives as long as they contain less than 0.3 percent delta-9 THC. In May 2022, the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals ruled that delta-8 THC met the definition of the Farm Law as a federally permitted hemp product.
Based on the wording of the Farm Bill and a later court decision, many growers consider THC-O to be a legal cannabis derivative as well. However, in February 2023, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) explained in a letter to cannabis attorney Rod Knight that the agency considers THC-O a Schedule 1 state-controlled drug.
The DEA may take enforcement action against manufacturers or sellers of THC-O at any time, including confiscation of products, arrests of employees, and charges against companies and individuals for violating the Controlled Substances Act.
THC-O products are sold online by many of the same retailers that sell CBD (and Delta 8, Delta 10, HHC and THCP). THC-O can also be found in convenience stores, convenience stores, gas stations, and some vape shops.
Why Is THC-O So Special?
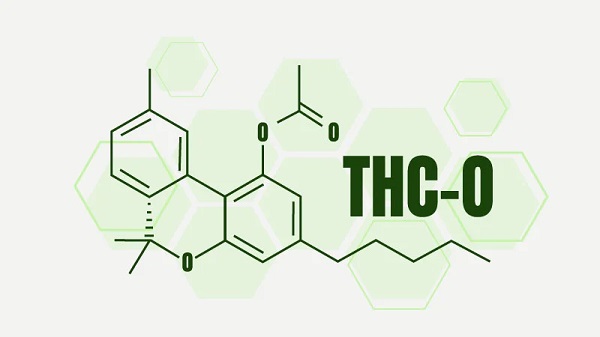
Adding an acetate molecule to the base THC molecule does one very important thing: it makes the THC molecule stronger. We know you’re itching to hear about the power of TGC-O, but hold your horses. Let’s talk about water solubility first, because there is a bit of confusion in this regard.
THC-O Is NOT Water Soluble
Cannabinoids such as THC and CBD are lipids (fatty oils) in their natural state. Thus, as a consumable product, they are fat-soluble (i.e., soluble in oil).
In our body, the dissolution of fats and oils occurs somewhat differently than the dissolution of water-soluble substances such as vitamins and fiber. Simply put, there is an additional filtration step before nutrients enter the bloodstream.
The difference in these processes means that when it comes to cannabis consumption, less THC enters the bloodstream (due to additional filtration) and ultimately the brain (where all the magic happens).
But water-soluble materials bypass this extra filtration step and go straight into the bloodstream. This means more nutrients are available for your body to use.
THC-O-phosphate, the cousin of THC-O, is soluble in water, but due to its chemical composition, it does not dissolve very quickly. This results in a slower onset of effects and reduced effectiveness than a conventional THC molecule. Why does anyone need it?
Does this mean that THC-O is also soluble in water? Unfortunately no. THC-O is insoluble in water. Your body is subjecting the molecule to the same filtering process as other fat-soluble molecules.
Because of these filters, you get a smaller percentage of molecules into your bloodstream when you consume a THC-O product. But there’s good news in all this confusion between water-soluble and water-insoluble: THC-O molecules are far more potent than regular smoked, mashed, or ingested THC.
This means that even though fewer THC-O molecules can enter your brain (due to the filtering process), the relatively few that get through knock you off your feet.
Why is THC-O considered to be so strong?
Lab tests show that THC-O can be up to 300 percent stronger than regular THC. Yes, you read that right: 300 percent stronger. And all this because of a tiny molecule of acetate! It makes you appreciate how powerful chemistry can be.
If you’re a thinking consumer, you might be wondering why anyone would want something so powerful. And you will be right. So let’s do away with the idea of recreational use of THC-O – regular THC is great for getting you high – and focus on medical uses instead. This is where THC-O really shines. It goes without saying that everyone is different. The biology of one person’s body is different from the biology of another person’s body. Thus, in some people, THC does not have the desired medical effect (pain relief, soothing, etc.).
However, THC-O is in every way a different version of the drug. Because of this, it can stimulate cannabinoid receptors in your brain in a way that regular THC cannot. So where a THC tablet or THC oil can’t provide the pain relief you’re looking for, a THC-O product can be a viable alternative. That’s why more and more people are talking about THC-O these days – because of its potential medical benefits.
So if you are thinking about trying THC-O for the first time, start small (preferably very small) and gradually increase the dosage. It’s hard to overdose on cannabinoids, but too much can take you too high and give you a bad ride. This is contrary to the purpose of all efforts.
What Can I Expect From THC-O?
One of the most important things you can do before using a product like THC O is to know your reaction to such a product. It is suggested that a person start at low doses in order to be aware of how their body is reacting and to actively make any necessary changes. It can take up to thirty minutes to feel the effect, so it’s important to wait before taking your second dose.
THC O is now taking the world by storm with its increased power and psychedelic effects. You can get more powerful and longer-lasting effects at moderate dosages, making it a great addition to your travel needs. Total body relaxation, intense highs, comfort and other substances are just some of the many health benefits you will get from the almighty THC O.
Summary
Based on the above information, it is rather difficult to unambiguously say about the unquestionable benefits of this product, however, experienced users can always correctly calculate their strengths, and most importantly, help beginners with this.
Should you try? Absolutely! Especially if you are looking for a specific medical benefit. THC-O might be just what you need. Having said that, it’s important to note that you should always buy THC-O from a reputable dealer.
Speak with specialists at your local dispensary. They can help you find just the right product. And please, please don’t try to make THC-O on your own. The process requires special equipment and advanced training. Volatile, flammable and explosive chemicals are needed.
It doesn’t cost your life (or your house, or your eyebrows) to do something that the lab can do better and safer. If you want to use THC-O, always buy, don’t make your own.